Jeep XJ. Manual - part 426
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve, clutch and servo operation. Foaming also
causes fluid expansion which can result in fluid over-
flow from the transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid
overflow can easily be mistaken for a leak if inspec-
tion is not careful.
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission
fluid
if
the
vehicle
is
improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
FLUID CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
• adding incorrect fluid
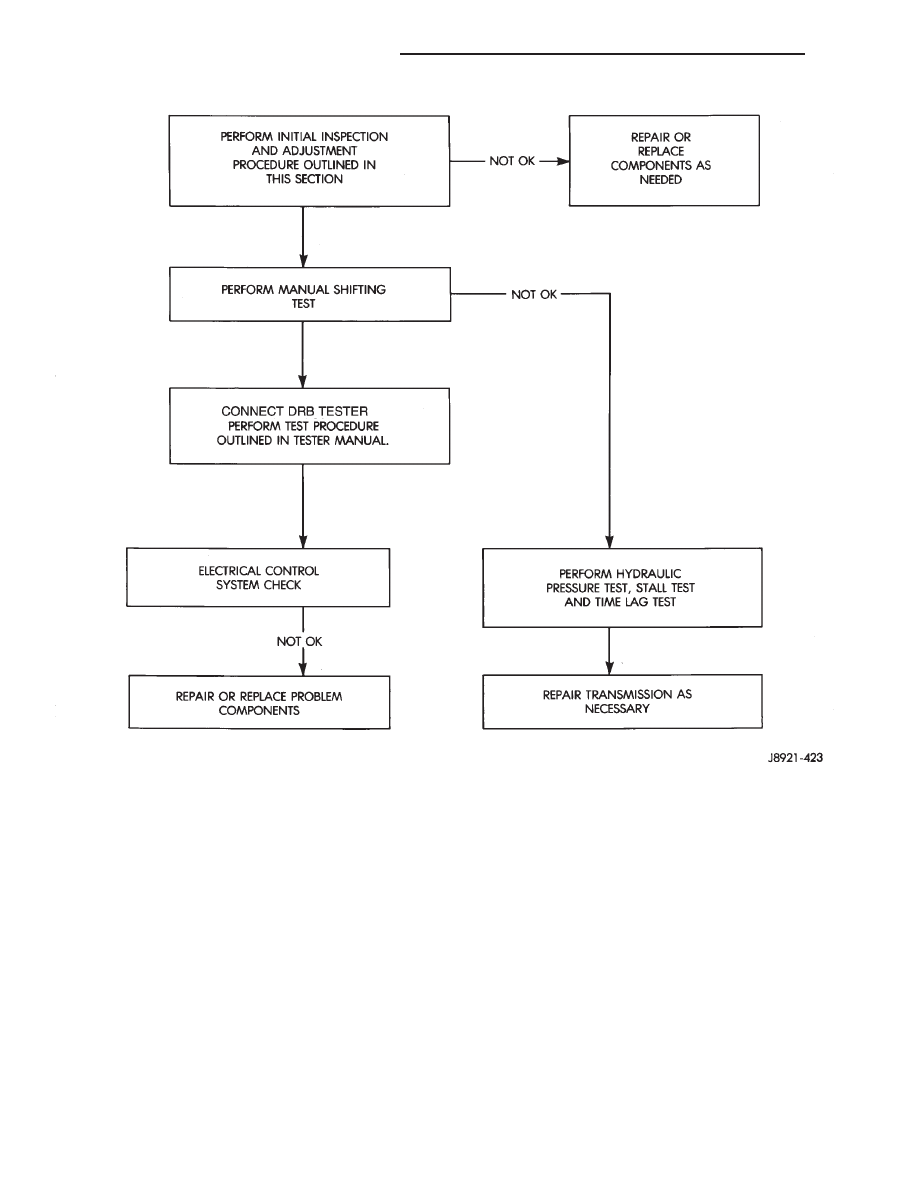
Preliminary Diagnosis Check Procedure
21 - 240
AW–4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
XJ
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)