Jeep Grand Cherokee WK. Manual - part 101
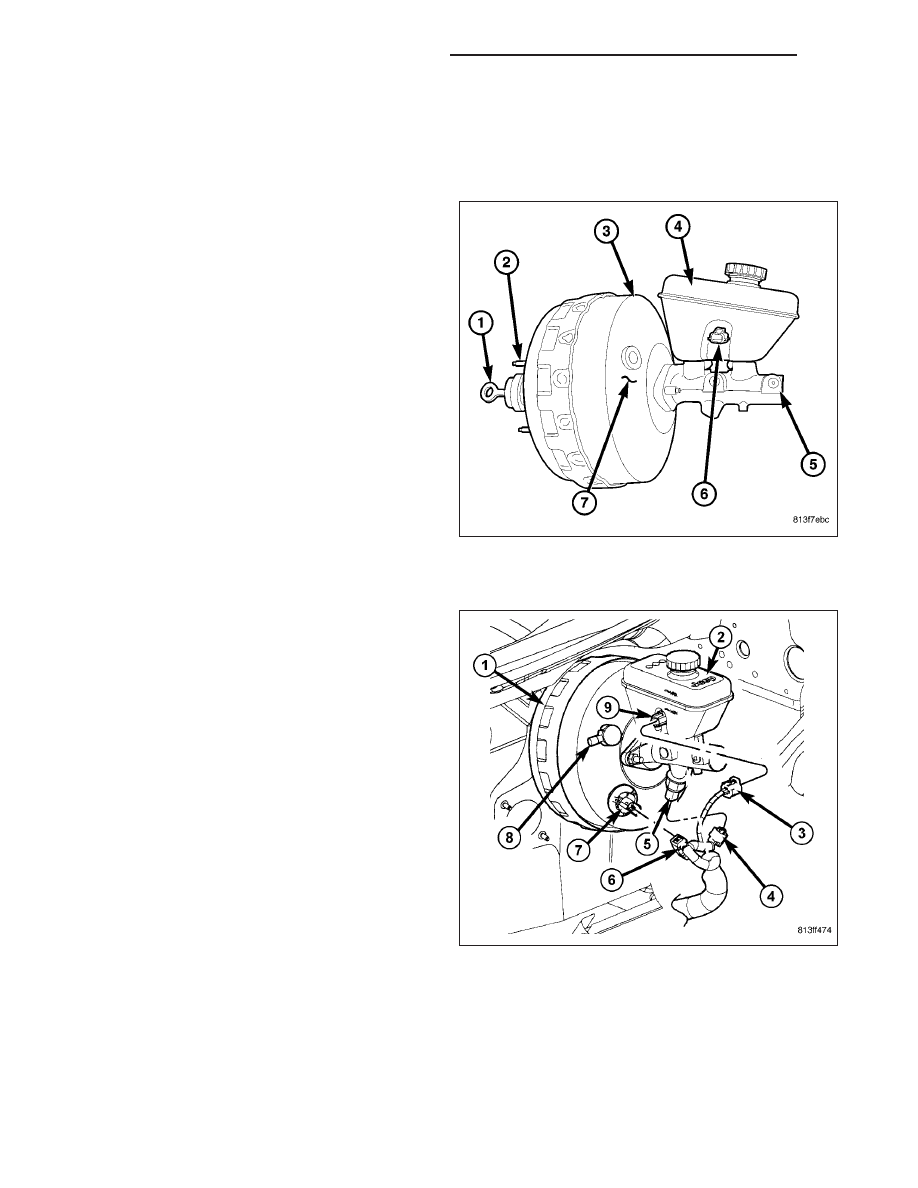
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
BASE MASTER CYLINDER WITHOUT ESP
The master cylinder body (5) is made of aluminum
and contains a primary and secondary piston assem-
bly. The cylinder body including the piston assemblies
are not serviceable. If diagnosis indicates an internal
problem with the cylinder body (5), it must be replaced
as an assembly. The master cylinder has a removable
reservoir (4) and fluid level indicator (6). The reservoir,
reservoir grommets, reservoir cap and fluid level
switch are the only replaceable parts on the master
cylinder.
MASTER CYLINDER WITH ESP
The master cylinder body is made of aluminum and
contains a primary and secondary piston assembly.
The cylinder body including the piston assemblies are
not serviceable. If diagnosis indicates an internal prob-
lem with the cylinder body, it must be replaced as an
assembly. The master cylinder with ESP has a pres-
sure switch (5) on the master cylinder. The reservoir
(2), reservoir grommets, reservoir cap, pressure switch
(5), solenoid connector (7) and fluid level switch (9)
are the only replaceable parts on the master cylinder.
OPERATION
The master cylinder bore contains a primary and secondary piston. The primary piston supplies hydraulic pressure
to the front brakes. The secondary piston supplies hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes. The master cylinder res-
ervoir stores reserve brake fluid for the hydraulic brake circuits.
5 - 30
BRAKES - BASE - SERVICE INFORMATION
WK