Jeep Grand Cherokee WJ. Manual - part 89
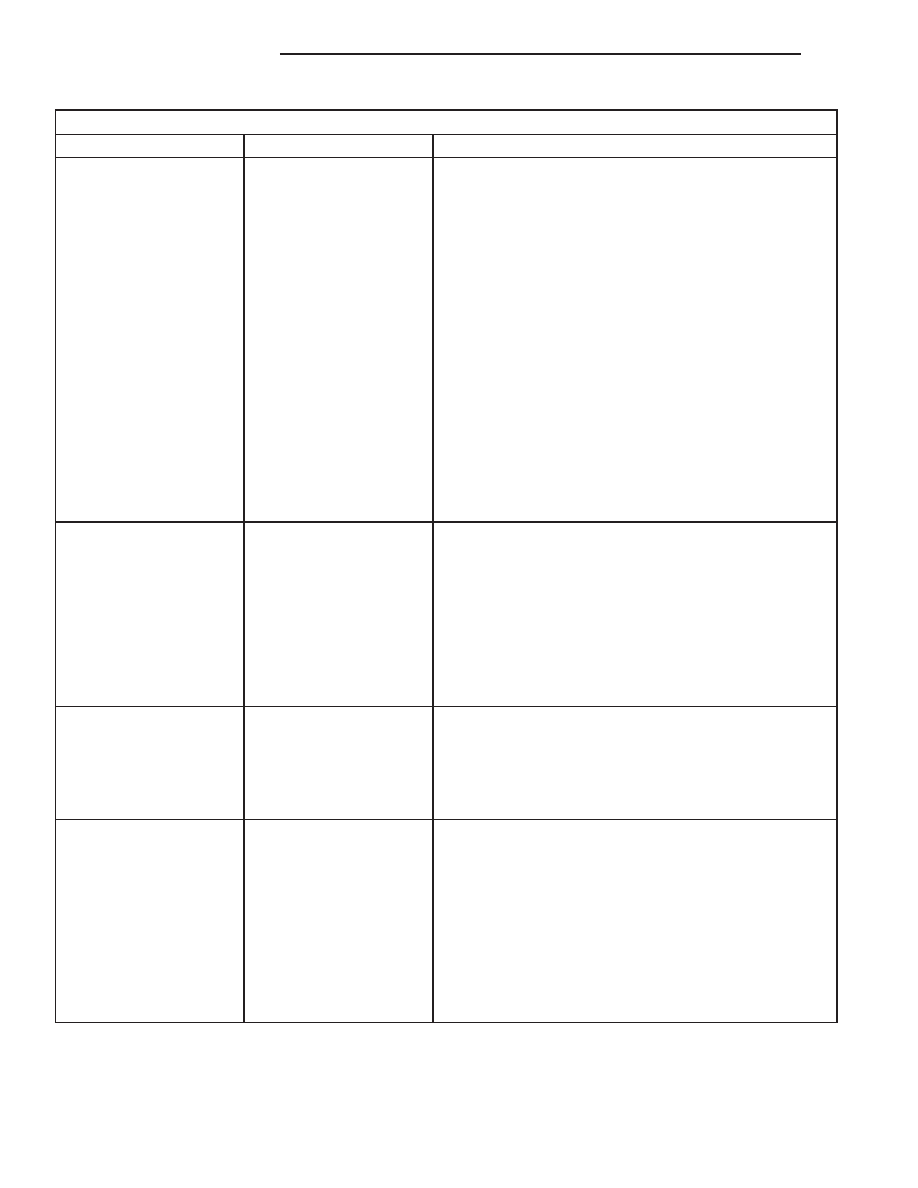
Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSE
CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
OPERATE.
1. Battery discharged or
faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.
3. Starter relay faulty.
4. Ignition switch faulty.
5. Park/Neutral position
switch faulty or
misadjusted.
6. Starter solenoid faulty.
7. Starter motor faulty.
1. Refer to Battery in the Diagnosis and Testing section of
Group 8A - Battery. Charge or replace the battery, if
required.
2. Refer to Starting System in Group 8W - Wiring
Diagrams. Test and repair the starter feed and/or control
circuits, if required.
3. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter relay, if
required.
4. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder in the
Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8D - Ignition
System. Replace the ignition switch, if required.
5. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch in the Diagnosis
and Testing section of Group 21 - Transmission. Replace
the park/neutral position switch, if required.
6. Refer to Starter Motor in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter motor assembly,
if required.
7. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.
1. Battery discharged or
faulty.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.
3. Starter motor faulty.
4. Engine seized.
1. Refer to Battery in the Diagnosis and Testing section of
Group 8A - Battery. Charge or replace the battery, if
required.
2. Refer to Starting System in Group 8W - Wiring
Diagrams. Test and repair the starter feed and/or control
circuits, if required.
3. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
4. Refer to Engine Diagnosis in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of Group 9 - Engine.
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.
1. Starter ring gear faulty.
2. Starter motor faulty.
1. Refer to Starter Motor in the Removal and Installation
section of this group. Remove the starter motor to inspect
the starter ring gear. Replace the starter ring gear, if
required.
2. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.
1. Starter motor
improperly installed.
2. Starter relay faulty.
3. Ignition switch faulty.
4. Starter motor faulty.
1. Refer to Starter Motor in the Removal and Installation
section of this group. Tighten the starter mounting
hardware to the correct tightness specifications.
2. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter relay, if
required.
3. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder in the
Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8D - Ignition
System. Replace the ignition switch, if required.
4. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
8B - 4
STARTING SYSTEMS
WJ
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)