Engine JAC HFC4DA1-2C. Manual - part 139
ABS
ABS
ABS
ABS Anti-lock
Anti-lock
Anti-lock
Anti-lock Brake
Brake
Brake
Brake System
System
System
System
- 77 -
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction
Instruction and
and
and
and Operation
Operation
Operation
Operation
Fault
Fault
Fault
Fault diagnosis
diagnosis
diagnosis
diagnosis procedures
procedures
procedures
procedures for
for
for
for ABS
ABS
ABS
ABS with
with
with
with EBD
EBD
EBD
EBD
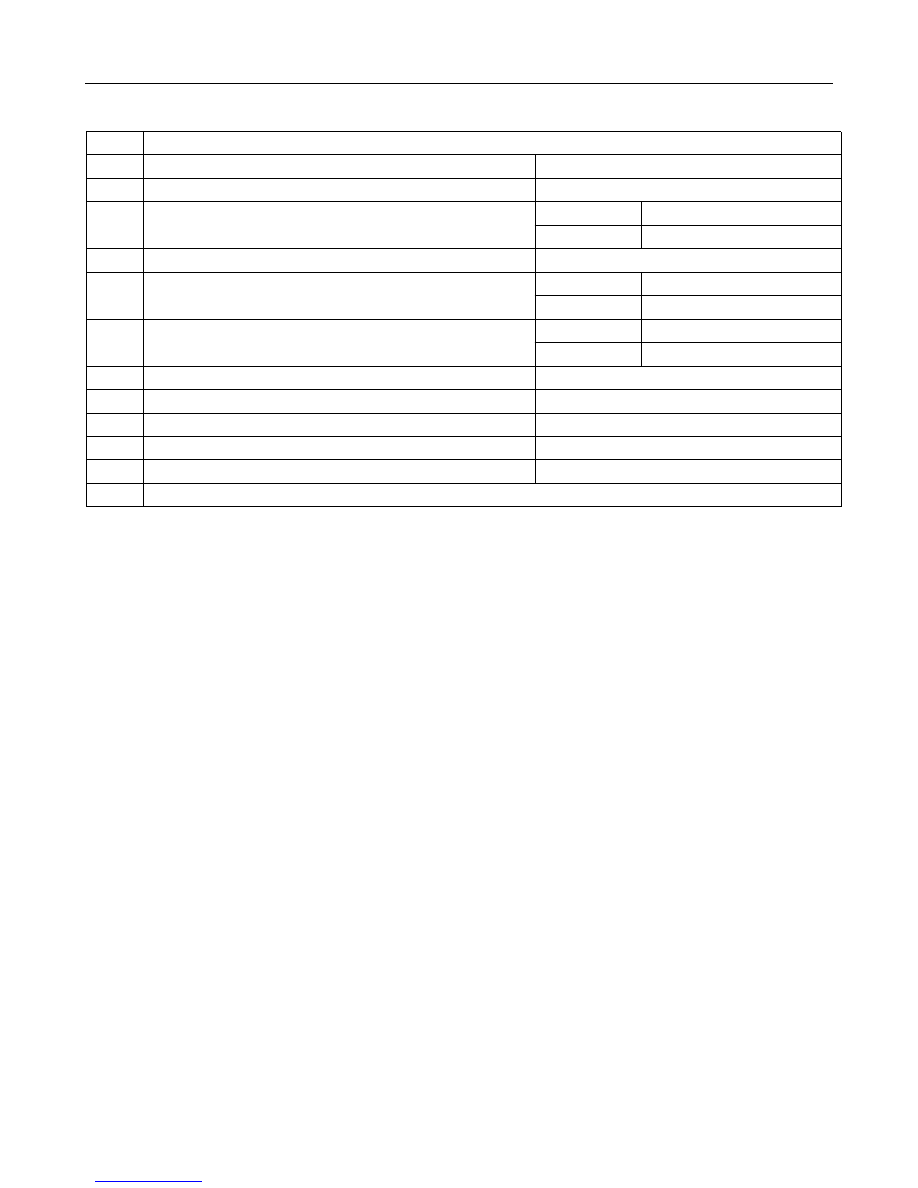
S/N
Operation
1
Drive the vehicle into repair shop.
Go to the next step.
2
Customer problem analysis
Go to the next step.
3
Read diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
With DTC
Go to Step 4
No DTC
Go to Step 9
4
Record DTC and clear fault memory.
Go to the next step.
5
Verify and reproduce fault: Simulation of fault occurrence status.
Read DTC again.
With DTC
Current DTC. Go to Step 8
No DTC
History DTC. Go to Step 6
6
Is it relevant to fault symptom?
Yes
Intermittent fault. Go to Step 7
No
Eliminated fault. Go to Step 9
7
Perform fault simulation again.
Go to the next step.
8
Perform troubleshooting based on DTC list. Go to Step 10.
Go to the next step.
9
Perform troubleshooting based on fault symptom list.
Go to the next step.
10
Ensure the fault is eliminated.
Go to the next step.
11
Prevention of recurrence.
Go to the next step.
12
End