Honda Odyssey 2004. Manual - part 508
→
→
→
―――
*07
*08
*09
*10
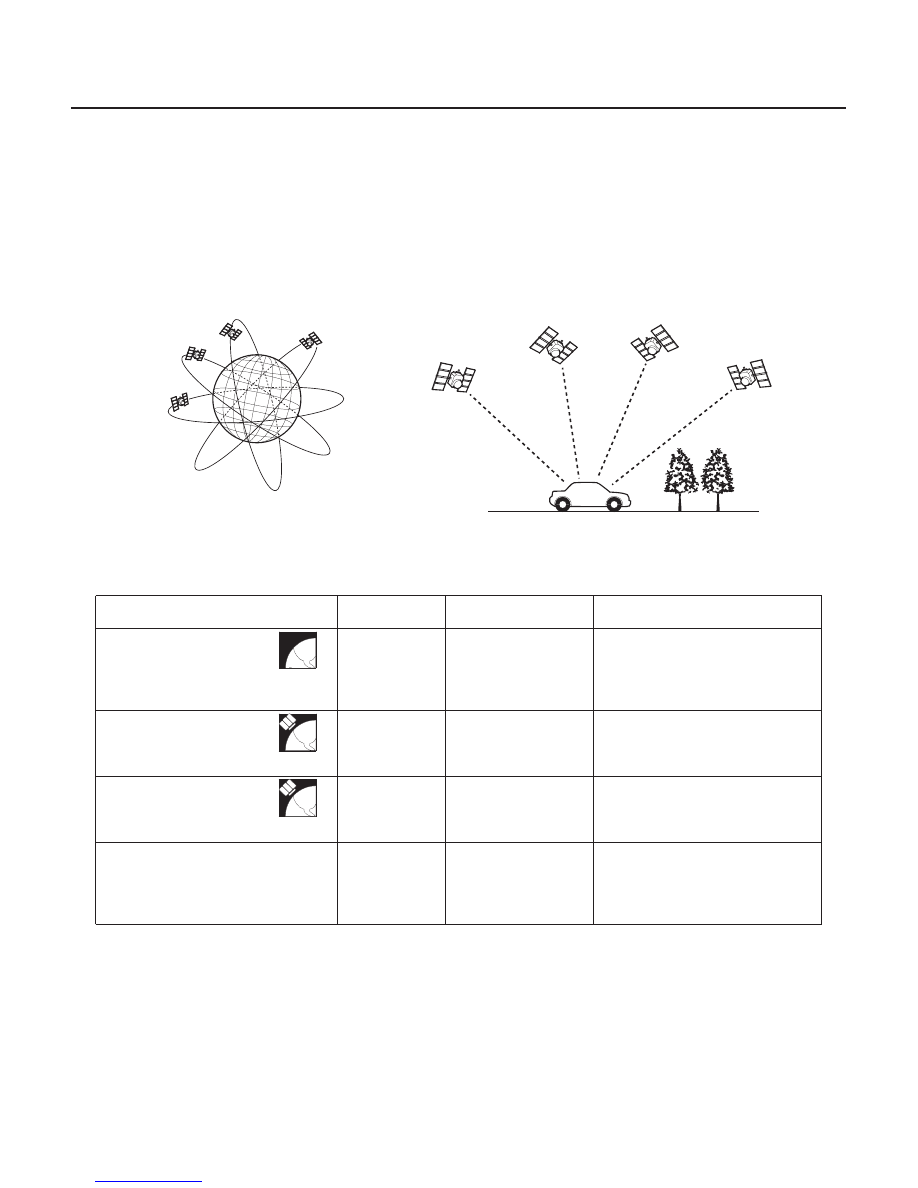
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Position detection Image with GPS satellite
Precision of GPS
GPS ICON
No.of
SATELLITES
CONDITION
DESCRIPTION
GPS Antenna
GPS Receiver
22-360
Navigation System
System Description (cont’d)
The global positioning system (GPS) enables the navigation system to determine the current position of the vehicle by
utilizing the electronic waves transmitted from the satellites in orbit around the earth. The satellites transmit the
satellite identification signal, orbit information, transmission time signal, and other information. When the GPS
receiver receives the electronic waves from three or more satellites simultaneously, it calculates the current position
of the vehicle based on the distance to each satellite and the satellite positions on their respective orbits.
The precision of the GPS varies according to the number of satellites from which electronic waves are received and
the control condition. The precision is indicated by the GPS mark shown on the upper left of the display.
No
satellite
mark
Two or less
Impossible to detect
vehicle position
The GPS function is normal.
The satellite electronic waves
received by the GPS receiver are
too few to determine the vehicle
position.
Yellow
satellite
mark
Three
Vehicle position
detectable in two
dimensions
The longitude and latitude of the
vehicle position can be
determined. (Less precise than
detection in three dimensions)
Green
satellite
mark
Four or more
Vehicle position
detectable in three
dimensions
The longitude, latitude and the
altitude of the vehicle position can
be determined. (More precise
than detection in two dimensions)
Not indicate
Faulty
The GPS can’t be utilized due to a
faulty GPS receiver, open in the
antenna wire, disconnected
antenna, or other outside
interference.
The GPS antenna amplifies and transmits the electronic waves received from the satellites, to the GPS receiver.
The GPS receiver is built into the navigation unit. It calculates the vehicle position by receiving the signal from the GPS
antenna. The vehicle position and signal reception condition is transmitted from the GPS receiver to the navigation
control unit to adjust the vehicle position.
NOTE: Four satellites on each of six orbits.
03/07/29 10:28:38 61S0X050_220_0362