Index Ford Ford F150 Pickup - service and repair instruction 2003 year
|
|
|
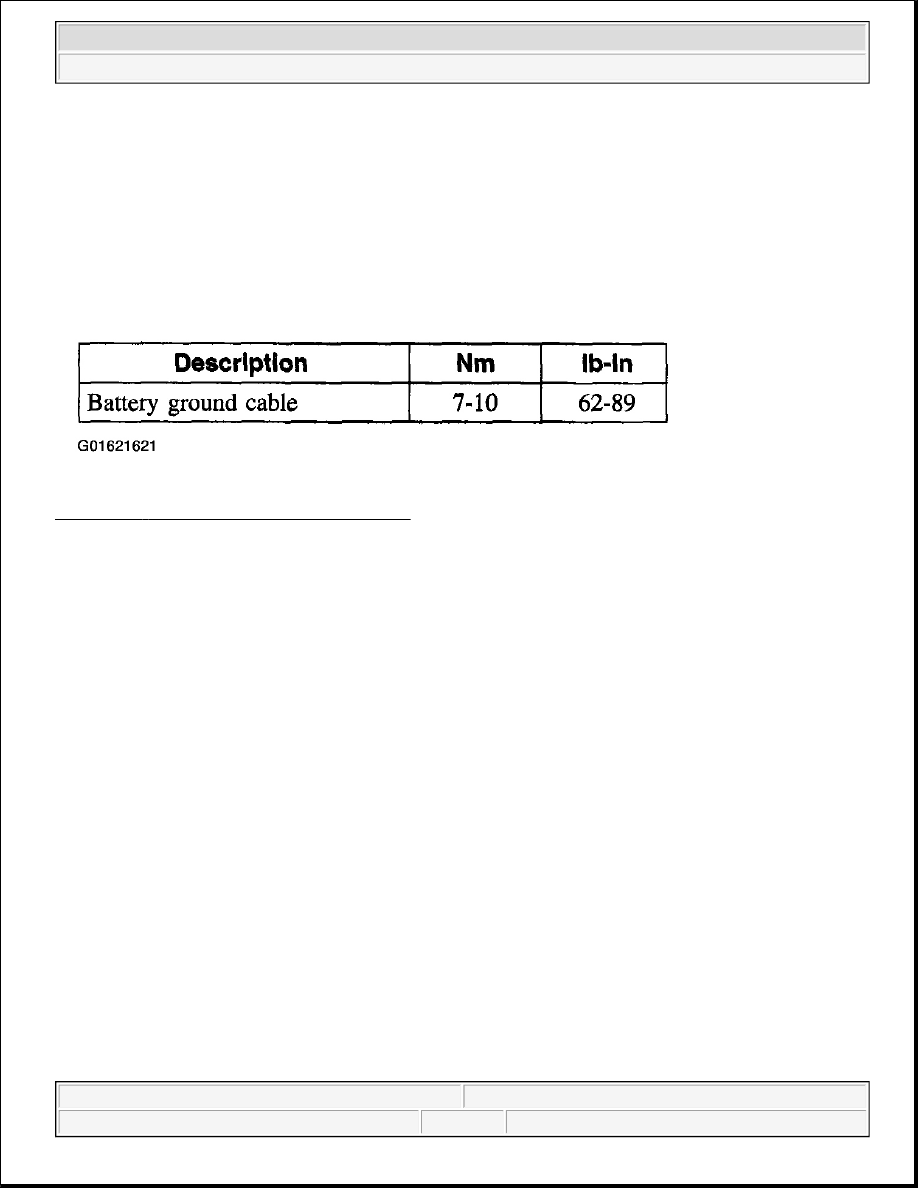
2003 ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Anti-Theft-PATS - F150 Pickup SPECIFICATIONS TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS Fig. 1: Anti-Theft - Pats Torque Specifications DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ANTI-THEFT - PATS The passive anti-theft system (PATS) contains the following components: z theft indicator z encoded ignition key z transceiver module z instrument cluster z powertrain control module (PCM) z standard corporate protocol (SCP) communication network The PATS uses radio frequency identification technology to deter a driveaway theft. Passive means that it does The PATS uses a specially encoded ignition key. Each encoded ignition key contains a permanently installed Each encoded ignition key must be programmed into the vehicle's instrument cluster (the instrument cluster is
2003 Ford Pickup F150 2003 ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Anti-Theft-PATS - F150 Pickup
2003 Ford Pickup F150 2003 ACCESSORIES AND EQUIPMENT Anti-Theft-PATS - F150 Pickup
|