Dodge Durango (DN). Manual - part 423
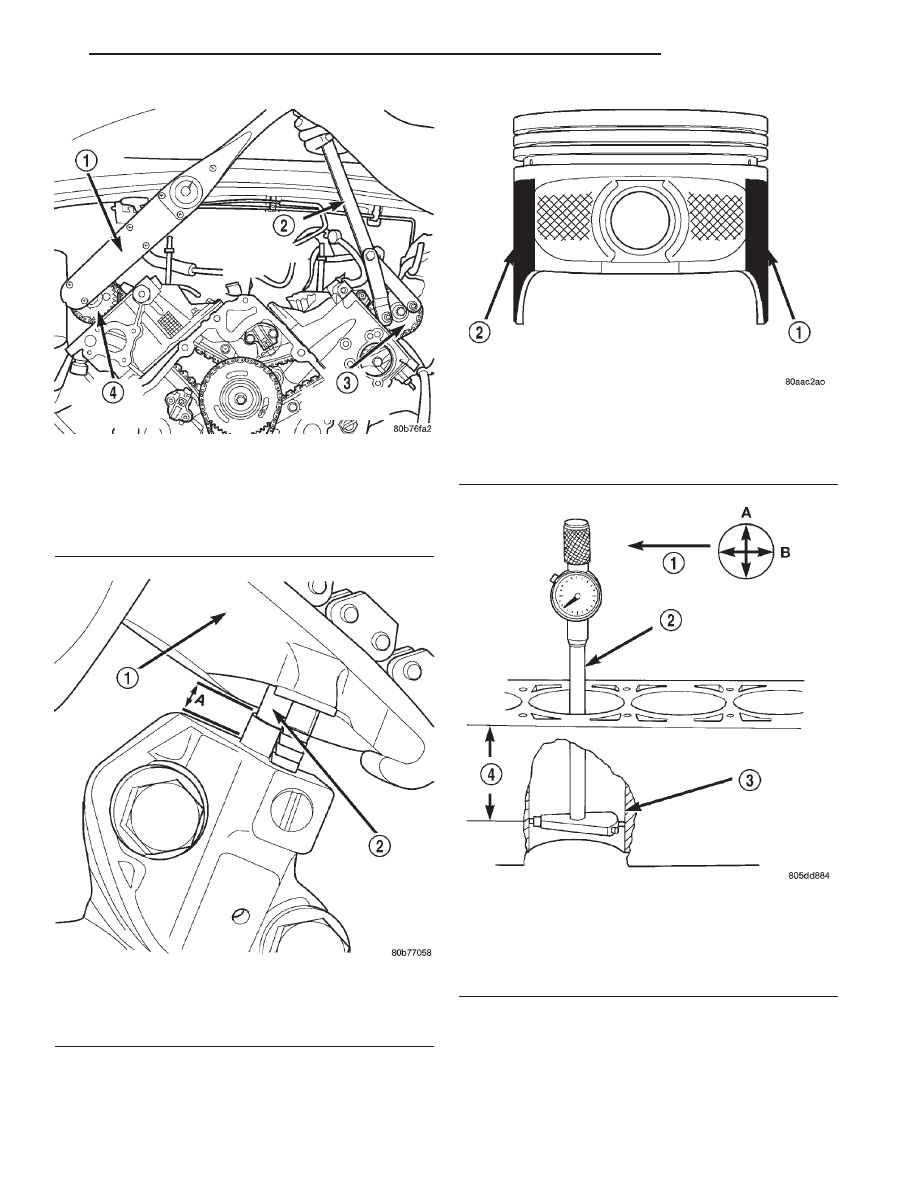
Fig. 16 Camshaft Sprocket Installation—Right
Cylinder Head
1 – TORQUE WRENCH
2 – SPECIAL TOOL 6958 WITH ADAPTER PINS 8346
3 – LEFT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
4 – RIGHT CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
Fig. 17 Measuring Secondary Timing Chains For
Stretch
1 – SECONDARY TENSIONER ARM
2 – SECONDARY CHAIN TENSIONER PISTON
Fig. 18 Moly Coated Piston
1 – MOLY COATED
2 – MOLY COATED
Fig. 19 Bore Gauge—Typical
1 – FRONT
2 – BORE GAUGE
3 – CYLINDER BORE
4 – 49.5 MM
(1–15/16 in)
DN
4.7L ENGINE
9 - 23
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)