Dodge Durango (DN). Manual - part 247
replacement procedure of the exciter ring, refer to
Group 3 Differential and Driveline.
OPERATION
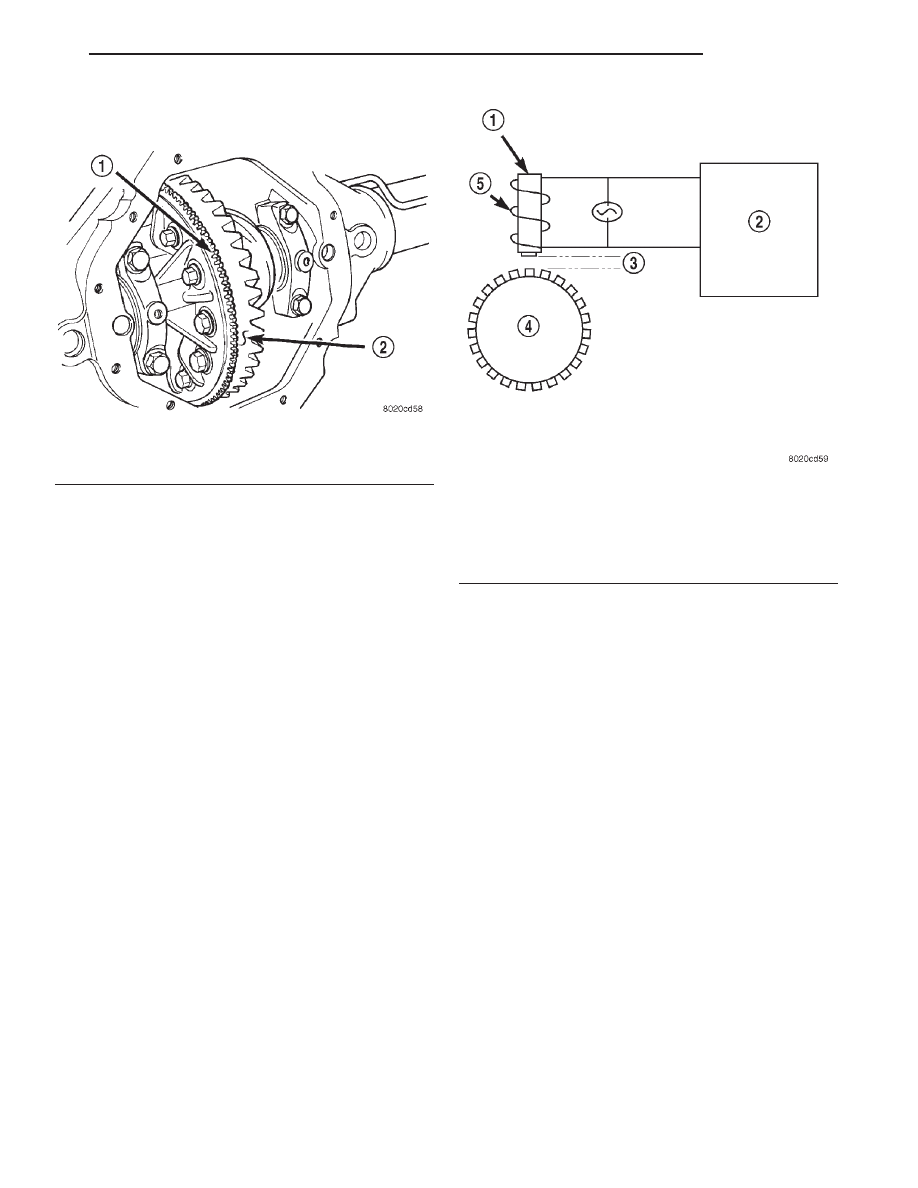
The WSS consists of a magnet surrounded by
windings from a single strand of wire. The sensor
sends a small AC signal to the CAB. This signal is
generated by magnetic induction. The magnetic
induction is created when a toothed sensor ring
(exciter ring or tone wheel) passes the stationary
magnetic WSS.
When the ring gear is rotated, the exciter ring
passes the tip of the WSS. As the exciter ring tooth
approaches the tip of the WSS, the magnetic lines of
force expand, causing the magnetic field to cut across
the sensor’s windings. This, in turn causes current to
flow through the WSS circuit (Fig. 4) in one direc-
tion. When the exciter ring tooth moves away from
the sensor tip, the magnetic lines of force collapse
cutting the winding in the opposite direction. This
causes the current to flow in the opposite direction.
Every time a tooth of the exciter ring passes the tip
of the WSS, an AC signal is generated. Each AC sig-
nal (positive to negative signal or sinewave) is inter-
preted by the CAB. It then compares the frequency of
the sinewave to a time value to calculate vehicle
speed. The CAB continues to monitor the frequency
to determine a deceleration rate that would indicate
a possible wheel-locking tendency.
The signal strength of any magnetic induction sen-
sor is directly affected by:
• Magnetic field strength; the stronger the mag-
netic field, the stronger the signal
• Number of windings in the sensor; more wind-
ings provide a stronger signal
• Exciter ring speed; the faster the exciter ring
rotates, the stronger the signal will be
• Distance between the exciter ring teeth and
WSS; the closer the WSS is to the exciter ring, the
stronger the signal will be
The rear WSS is not adjustable. A clearance speci-
fication has been established for manufacturing toler-
ances.
If
the
clearance
is
not
within
these
specifications, then either the WSS or other compo-
nents may be damaged. The clearance between the
WSS and the exciter ring is 0.005 – 0.050 in.
The assembly plant performs a “Rolls Test” on
every vehicle that leaves the assembly plant. One of
the test performed is a test of the WSS. To properly
test the sensor, the assembly plant connects test
equipment to the Data Link Connector (DLC). This
connector is located to the right of the steering col-
umn and attached to the lower portion of the instru-
ment panel (Fig. 5). The rolls test terminal is spliced
to the WSS circuit. The vehicle is then driven on a
set of rollers and the WSS output is monitored for
proper operation.
BRAKE WARNING LAMPS
DESCRIPTION
The red brake warning lamp and amber ABS
warning lamp are located in the instrument cluster.
The red brake warning lamp is used to alert the
driver of a hydraulic fault or that the parking brake
is applied. For the RWAL system, the red brake
Fig. 3 Exciter Ring Location
1 – EXCITER RING
2 – RING GEAR
Fig. 4 Operation of the Wheel Speed Sensor
1 – MAGNETIC CORE
2 – CAB
3 – AIR GAP
4 – EXCITER RING
5 – COIL
DN
BRAKES
5 - 35
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)