Chrysler PT Cruiser. Manual - part 436
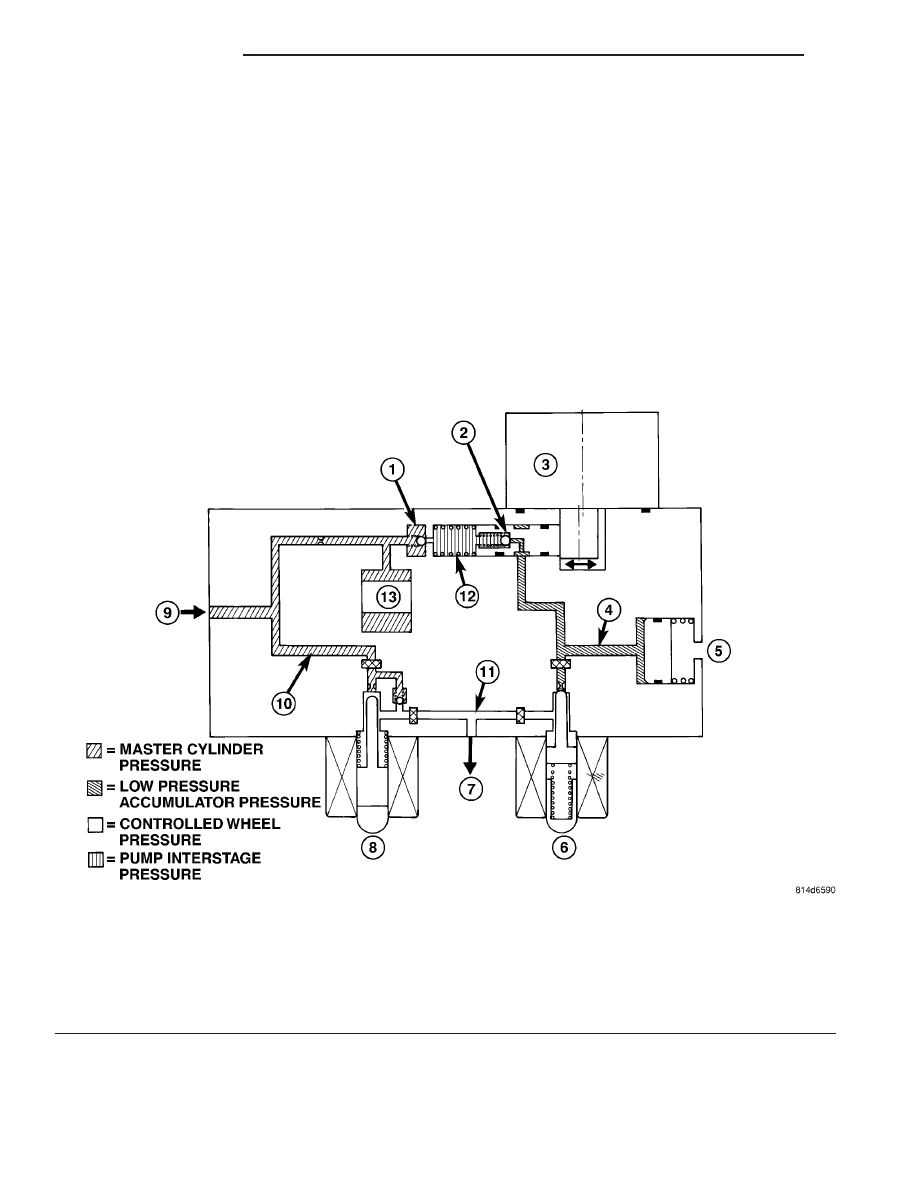
ABS HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT AND SOLENOID VALVE
FUNCTION (ABS WITHOUT TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram shows the vehicle in the
ABS braking mode (Fig. 15). The diagram shows one
wheel is slipping because the driver is attempting to
stop the vehicle at a faster rate than is allowed by
the surface on which the tires are riding.
• The normally open and normally closed valves
modulate (build/decay) the brake hydraulic pressure
as required.
• The pump/motor is switched on so that the
brake fluid from the low pressure accumulators is
returned to the master cylinder circuits.
• The brake fluid is routed to either the master
cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the posi-
tion of the normally open valve.
Fig. 15 Hydraulic Circuit - ABS Braking Mode (Without Traction Control)
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP/MOTOR (ON)
4 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR PRESSURE
5 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
6 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (MODULATING)
7 - TO WHEEL BRAKE
8 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (MODULATING)
9 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
10 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
11 - CONTROLLED WHEEL PRESSURE
12 - PUMP INTERSTAGE PRESSURE
13 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
5 - 96
BRAKES - ABS
PT
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (HCU) (Continued)