Chery Tiggo. Manual - part 5
DIAGNOSING ELECTRICAL FAILURES
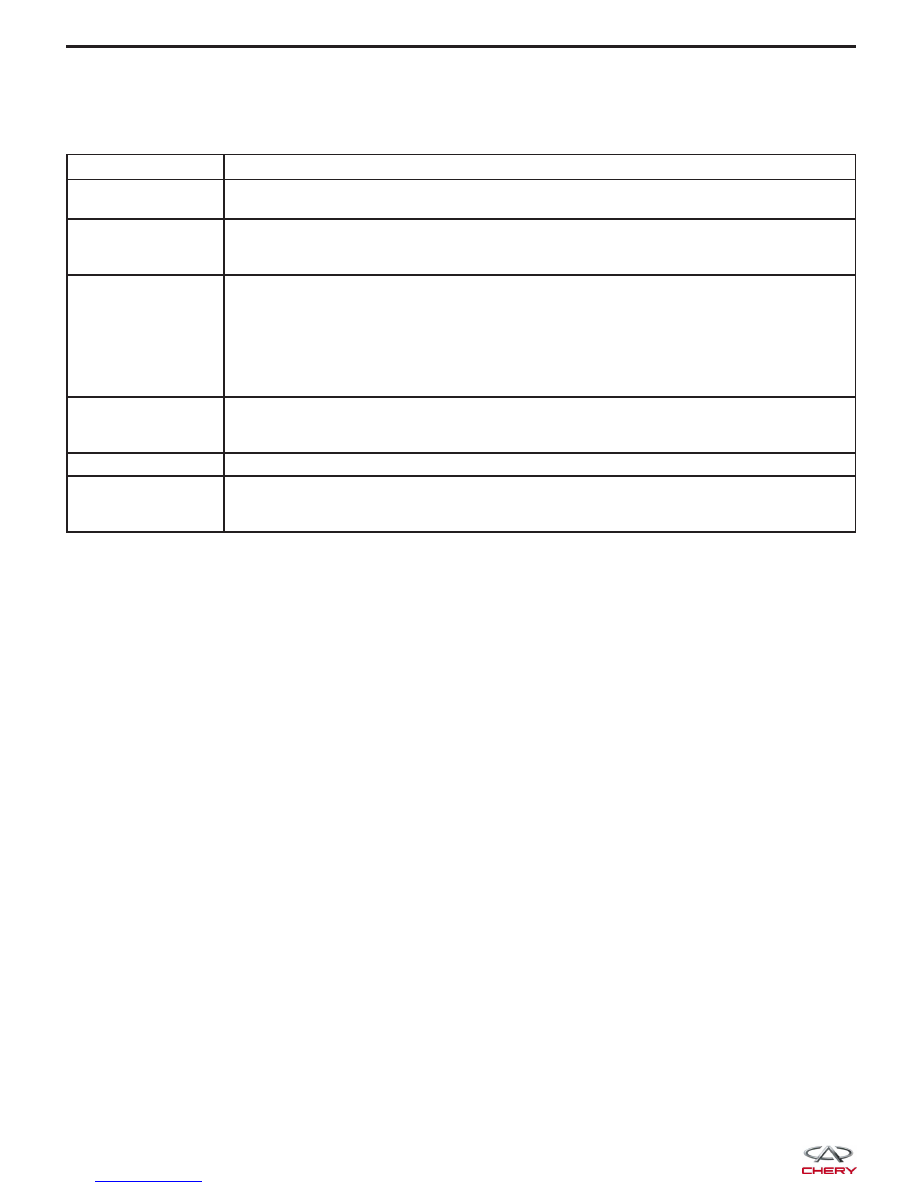
Performing Efficient Electrical Circuit Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
STEP
DESCRIPTION
Step 1
Obtain detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the electrical
incident occurred.
Step 2
Operate the affected system, road test the vehicle if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Electrical Failure Simulation Tests”.
Step 3
Gather the proper diagnostic material including the following:
• Electrical Power Supply Routing Diagram
• System Operation Descriptions
• Applicable Service Manual Sections
• Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation
and the customer comments.
Step 4
Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Electrical
Power Supply Routing Diagram and Harness Layouts.
Step 5
Repair the circuit or replace the component as necessary.
Step 6
Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system functions properly under all conditions.
Confirm you have not inadvertently created an additional new incident during your
diagnosis or repair steps.
Electrical Circuit Simulation Tests
Often the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the conditions
present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The following illustrates
tests to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an electrical incident.
The tests are broken into the seven following topics:
• Vehicle Vibration Test
• Heat Sensitive Test
• Freezing Test
• Water Intrusion Test
• Electrical Load Test
• Cold or Hot Start Up Test
• Voltage Drop Test
NOTE :
Always get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of
the problem.
Vehicle Vibration Test
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when the engine is vibrating (idle with A/C
on). In such a case, check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following vehicle areas:
Connectors & Harness
• Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to duplicate. This
test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
NOTE :
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible for a thin film of corrosion to form on the connector terminals.
A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs intermittently, per-
haps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the terminals on related
connectors in the system.