Challenger Terra Gator 3244 Chassis. Manual - part 25
627333-A
3-13
Transmission and Solenoids
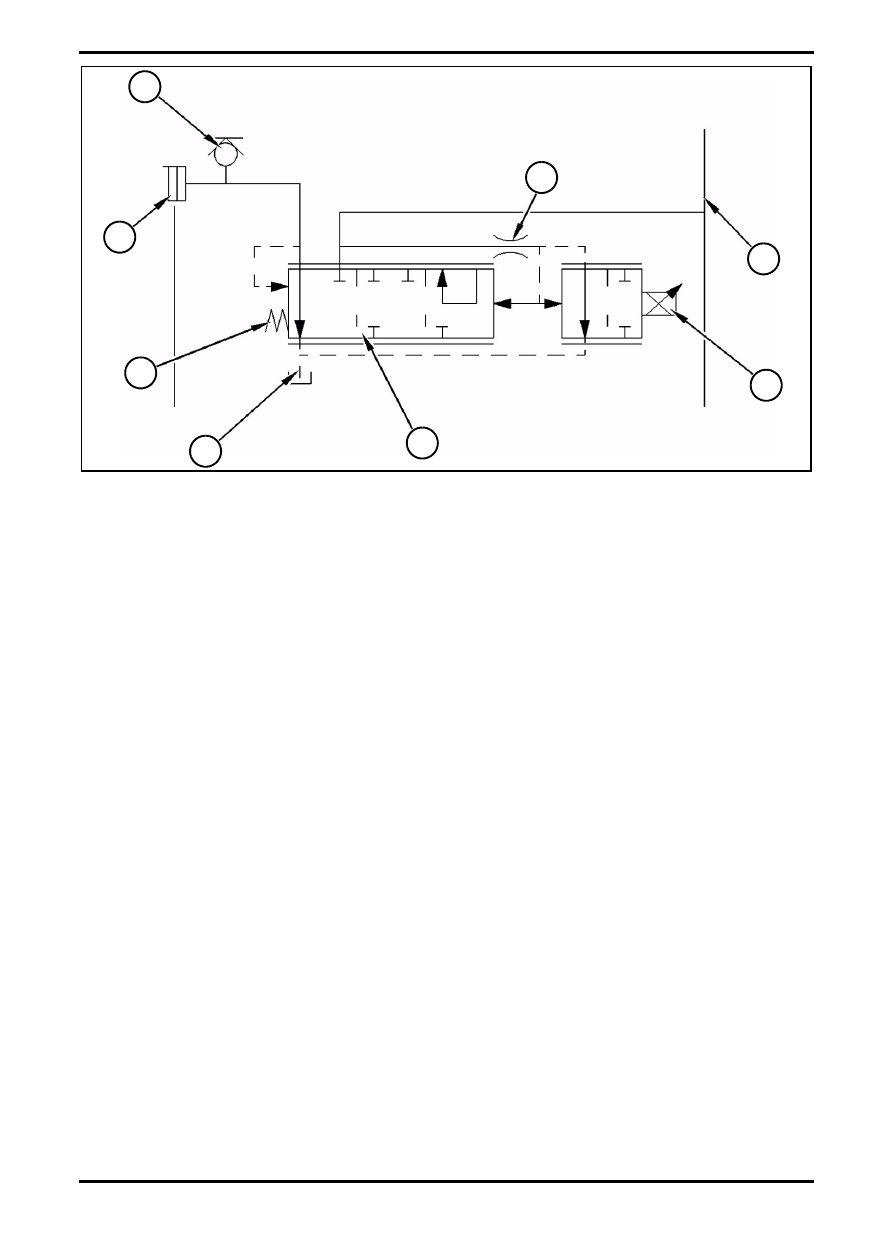
Schematic of modulating valve (transmission)
1. Modulating Valve (Transmission);
2. Test Port;
3. Transmission Clutch;
4. Spring;
5. Line to Sump;
6. Spool Orifice;
7. Charge Pressure Oil;
8. Solenoid.
Modulating valve (1) is controlled by transmission
electronic control module (ECM). The modulating valve
is used by the transmission ECM to directly modulate
the oil pressure that is sent to each of the nine
individual transmission clutches.
When the operator selects a direction or when the
operator selects a speed, the transmission ECM sends
a pulse width modulated signals in order to vary the
current to solenoid (8).
The distance that is travelled by the solenoid plunger is
proportional to the electrical current that is sent to the
solenoid. The position of the solenoid plunger controls
the oil pressure the is sent to transmission clutch (3).
When the transmission ECM sends the maximum
programmed current to the modulating valve, the
pressure in the transmission clutch will be at the
maximum desired pressure. When no current is sent to
the modulating valve, the oil pressure in the
transmission clutch will be zero.
FIG. 13
Q000038S
2
3
4
5
1
8
7
6