Nissan Versa Note. Manual - part 797
TM-68
< SYSTEM DESCRIPTION >
[CVT: RE0F11A]
STRUCTURE AND OPERATION
STRUCTURE AND OPERATION
TRANSAXLE
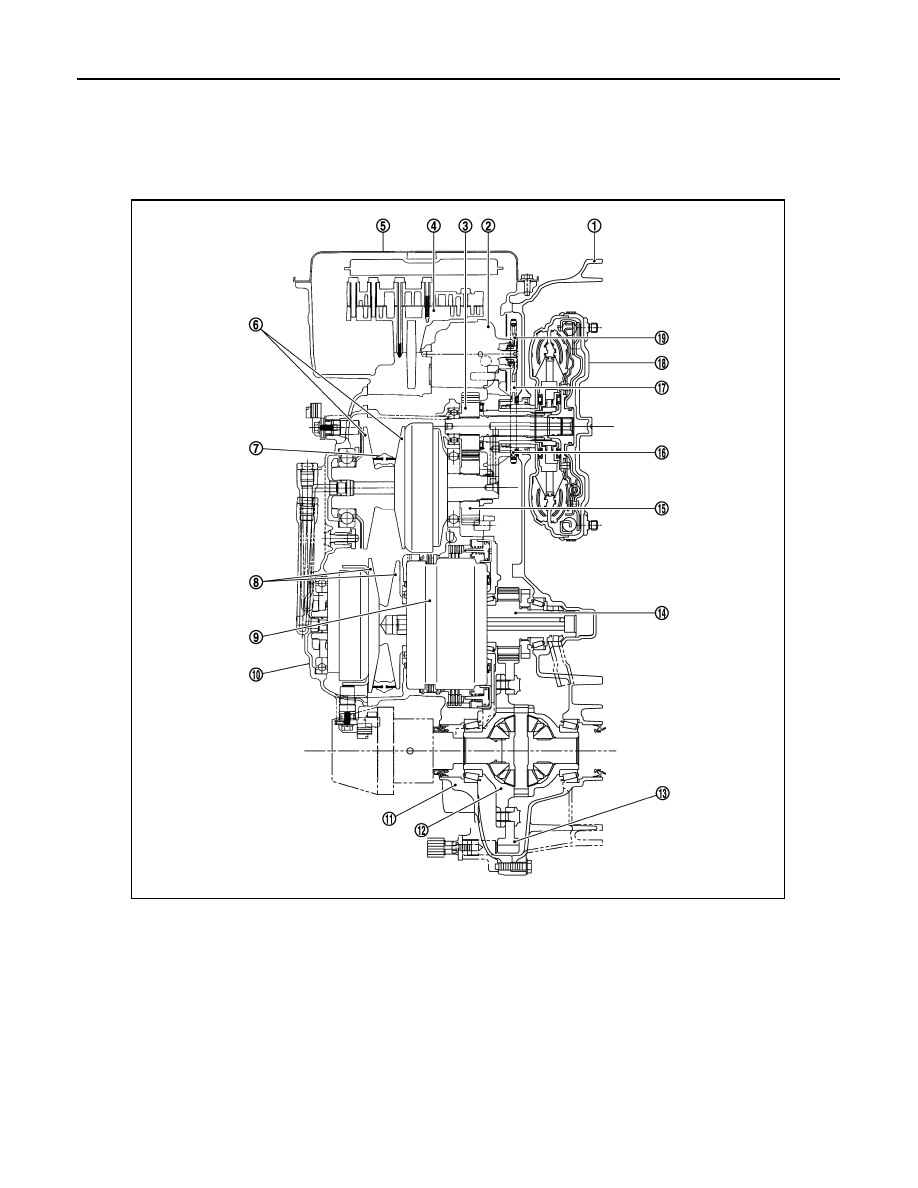
TRANSAXLE : Cross-Sectional View
INFOID:0000000009019604
TRANSAXLE : Transaxle Mechanism
INFOID:0000000009019605
BELT & PULLEY
1.
Converter housing
2.
Oil pump
3.
Counter drive gear
4.
Control valve
5.
Oil pan
6.
Primary pulley
7.
Steel belt
8.
Secondary pulley
9.
Planetary gear (auxiliary gearbox)
10.
Side cover
11.
Transaxle case
12.
Differential case
13.
Final gear
14.
Reduction gear
15.
Counter driven gear
16.
Drive sprocket
17.
Oil pump chain
18.
Torque converter
19.
Driven sprocket
JSDIA1777ZZ