Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution 7. Manual - part 204
MPI -
Troubleshooting
13A-115
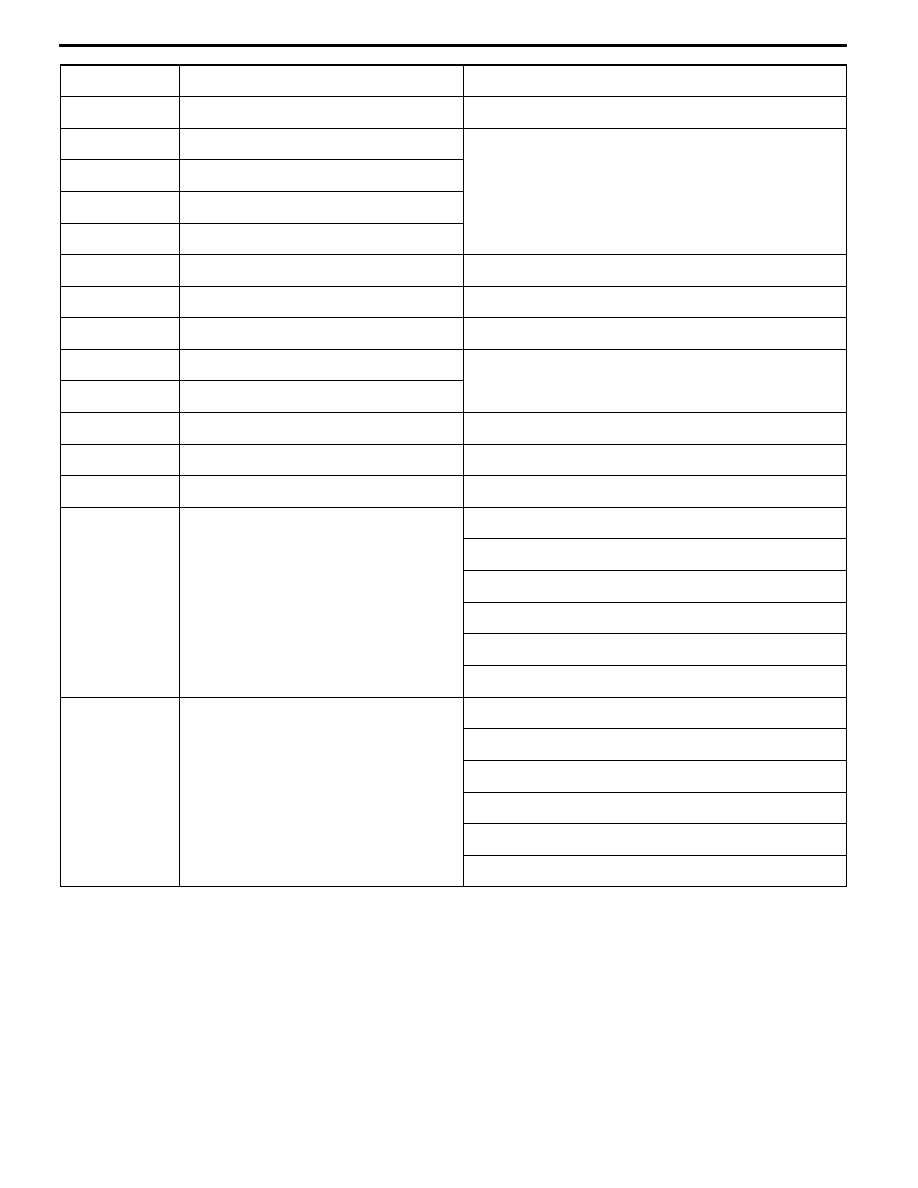
Terminal No.
Normal condition (Check condition)
Inspection item
3- 12
Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
28 - 36 Ω (at 20_C)
4- 12
Stepper motor coil (A1)
28 - 33 Ω (at 20_C)
17- 12
Stepper motor coil (A2)
5- 12
Stepper motor coil (B1)
18- 12
Stepper motor coil (B2)
6- 12
EGR control solenoid valve
36 - 44 Ω (at 20_C)
9- 12
Purge control solenoid valve
22 - 26 Ω (at 20_C)
11- 12
Waste gate solenoid valve
62 - 74 Ω (at 20_C)
13- Body earth
ENGINE-ECU earth
Continuity (0Ω)
26-Body earth
ENGINE-ECU earth
53- 12
Secondary air control solenoid valve
28 - 36 Ω (at 20_C)
54- 12
Oxygen sensor heater (Rear)
11 - 18 Ω (at 20_C)
60- 12
Oxygen sensor heater (Front)
4.5 - 8.0 Ω (at 20_C)
72- 92
Intake air temperature sensor
13 - 17 kΩ (When intake air temperature is -20_C)
5.7 - 6.7 kΩ (When intake air temperature is 0_C)
2.3 - 3.0 kΩ (When intake air temperature is 20_C)
1.0 - 1.5 kΩ (When intake air temperature is 40_C)
0.56 - 0.76 kΩ (When intake air temperature is 60_C)
0.30 - 0.42 kΩ (When intake air temperature is 80_C)
83- 92
Engine coolant temperature sensor
14 - 17 kΩ (When coolant temperature is -20_C)
5.1 - 6.5 kΩ (When coolant temperature is 0_C)
2.1 - 2.7 kΩ (When coolant temperature is 20_C)
0.9 - 1.3 kΩ (When coolant temperature is 40_C)
0.48 - 0.68 kΩ (When coolant temperature is 60_C)
0.26- 0.36 kΩ (When coolant temperature is 80_C)