Mazda Training manual - part 6
Powertrain Engines
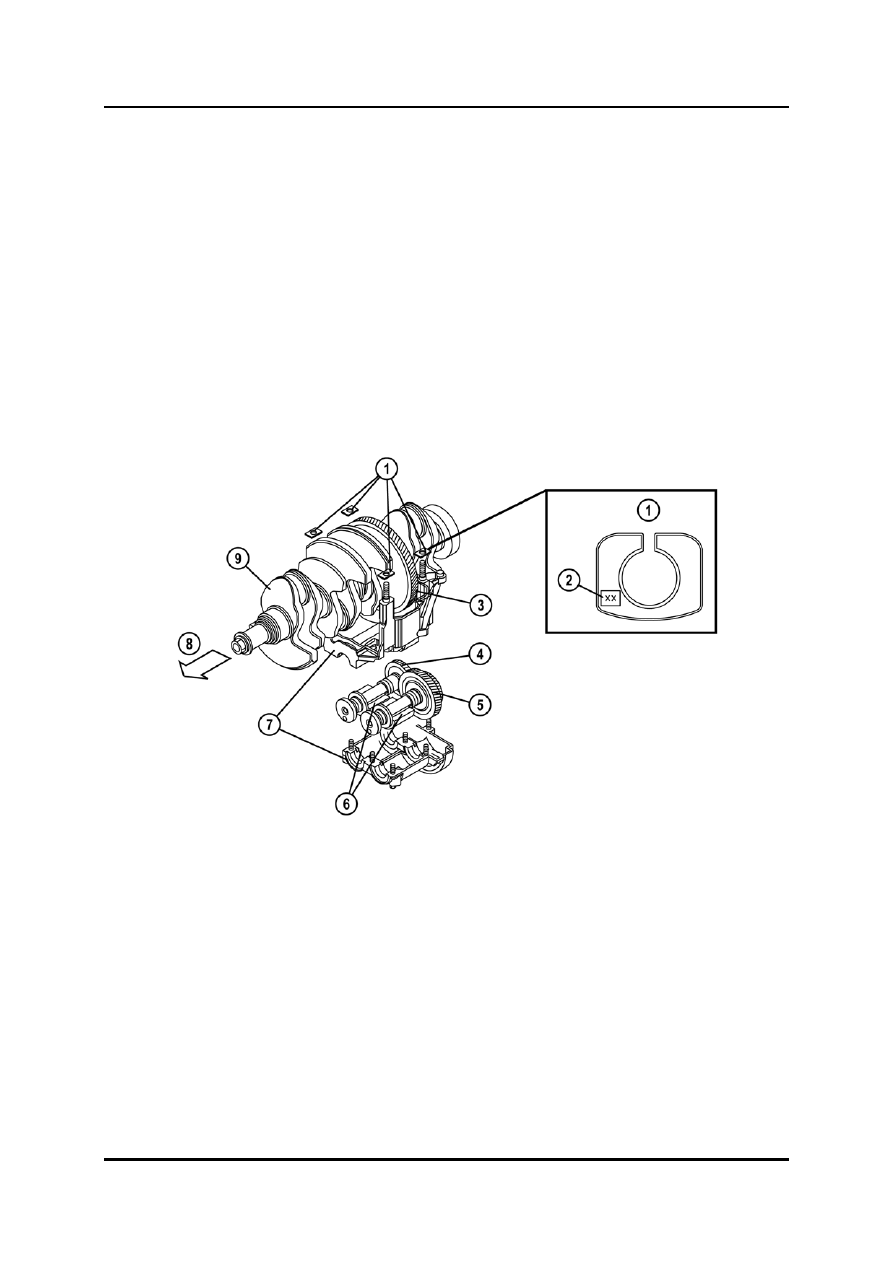
Balancer Shaft Unit
•
The balancer shafts minimize the engine vibrations by rotating at twice the speed of the
crankshaft.
•
The balancer shaft unit features a two-piece housing, which is fixed to the cylinder block
by four bolts.
NOTE: The balancer shaft unit cannot be repaired due to its precise interior construction, i.e.
it must be replaced as a complete unit.
•
If the cylinder block, crankshaft, crankshaft main bearing, or balancer shaft unit have
been replaced, the backlash between the drive gear of the crankshaft and the driven
gear of the balancer shaft unit must be adjusted using shims (refer to the workshop
manual for details).
L1001.4_01006
1
Adjustment shim
6
Counter weights
2
Engraved identification mark
7
Balancer shaft unit housing
3
Drive gear
8
Engine front side
4 Balancer
shaft
no.2
9 Crankshaft
5
Balancer shaft no.1 with driven gear
Curriculum Training
01-11