Land Rover Discovery. Manual - part 89
V8i
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COOLING
Description
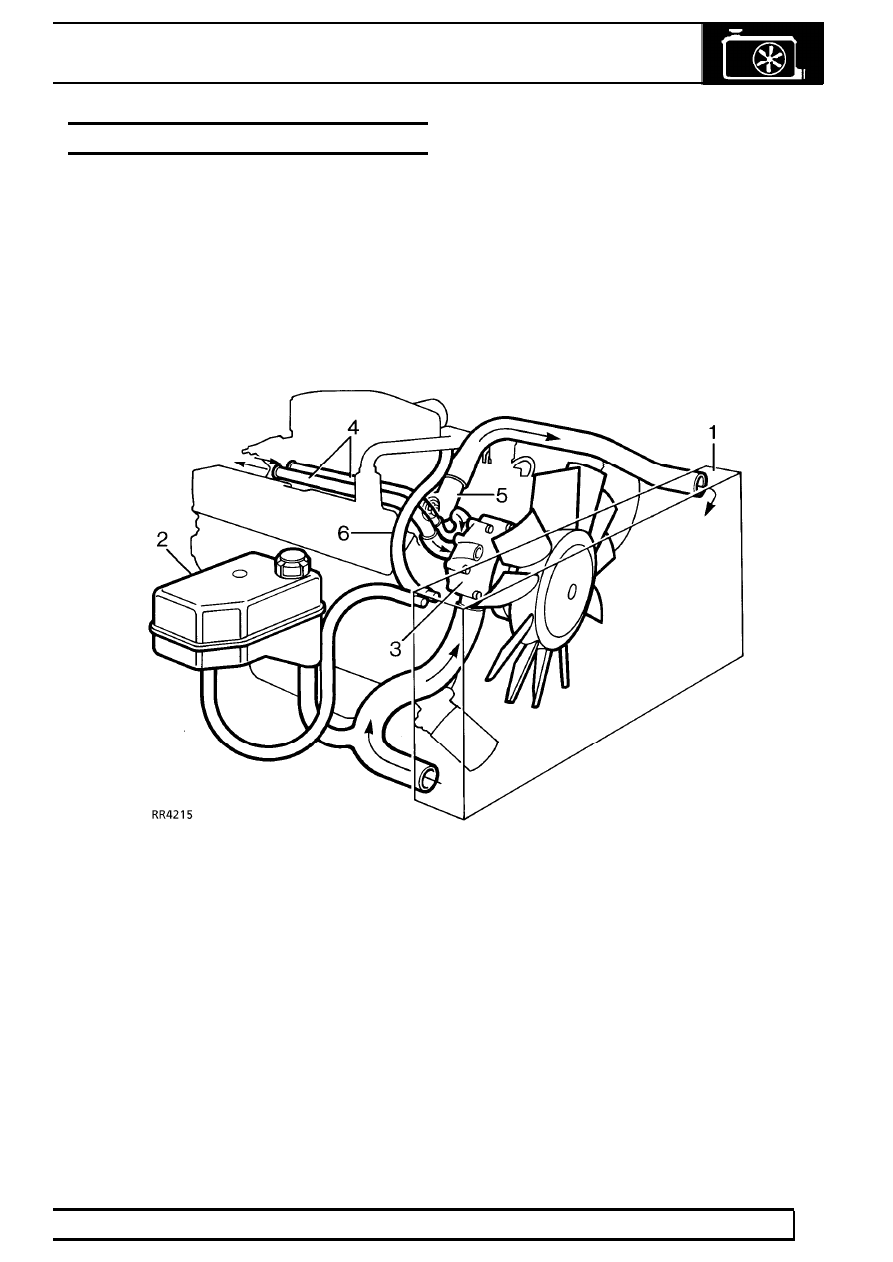
The V8i engine uses a pressurised cooling system
and cross flow radiator which is supplied from a
separate header tank. The coolant radiator also
incorporates a section at the left hand end for cooling
the transmission oil and a section at the other end for
cooling the engine oil.
The belt driven viscous fan and centrifugal water
pump is located in the engine front cover with ports for
circulation of coolant to both banks of cylinders and
cylinder heads. Coolant returns to the top of the
radiator via ports in the inlet manifold where the
thermostat is mounted horizontally.
Coolant also circulates through the vehicle heating
system and is used to heat air entering the inlet
manifold plenum chamber.
Coolant circulation (engine hot)
1. Cross flow radiator
2. Header tank
3. Viscous fan and water pump
4. Heater pipes
5. Plenum chamber connection
6. Thermostat