Jeep Grand Cherokee WJ. Manual - part 62
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the malfunction
indicator lamp. This lamp is displayed on the instru-
ment panel as the CHECK ENGINE lamp (Fig. 17).
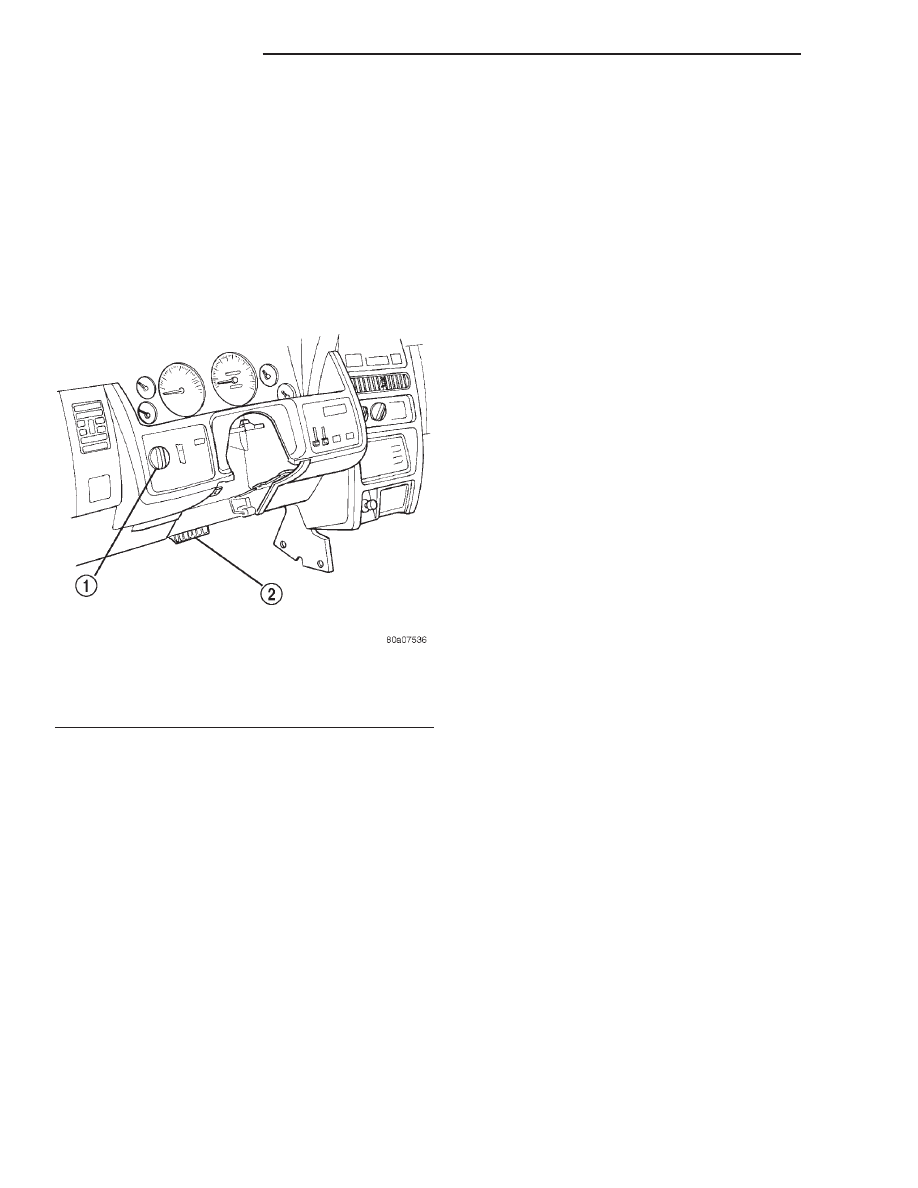
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
connects to the data link connector, left of the steer-
ing column above the brake pedal (Fig. 18). For oper-
ation of the DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual.
EXAMPLES:
• If the lamp (Fig. 17) flashes 1 time, pauses and
flashes 2 more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) number 12 is indicated. If this code is
observed, it is indicating that the battery has been
disconnected within the last 50 key-on cycles. It
could also indicate that battery voltage has been dis-
connected to the PCM. In either case, other DTC’s
may have been erased.
• If the lamp flashes 1 time, pauses and flashes 7
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 17 is indicated.
After
any
stored
DTC
information
has
been
observed, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored
information.
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
scan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice manual.
WATER PUMP TESTS
LOOSE IMPELLER—4.0L and 4.7L
NOTE: Due to the design of the 4.0L and 4.7L
engine water pumps, testing the pump for a loose
impeller must be done by verifying coolant flow in
the radiator. To accomplish this refer to the follow-
ing procedure.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(1) Drain coolant until the first row of cores is vis-
ible in the radiator.
(2) Leaving the radiator cap off, start the engine
(3) While looking into the radiator through the
radiator fill neck, raise engine rpm to 2000 RPM.
Observe the flow of coolant from the first row of
cores.
(4) If there is no flow or very little flow visable,
replace the water pump.
INSPECTING FOR INLET RESTRICTIONS
Inadequate heater performance may be caused by
a metal casting restriction in the heater hose inlet.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO
NOT
LOOSEN
THE
RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to
decrease the level below the heater hose inlet. On
4.7L engines this requires complete draining.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
NOTE: On 4.0L engines remove the pump from the
engine before removing restriction to prevent con-
tamination of the coolant with debris. Refer to
Water Pump Removal in this section. On 4.7L
engine remove the fitting from the timing chain
cover, If the restriction is in the timing chain cover,
remove the timing chain cover. Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in Group 9 Engine, for procedure.
Fig. 18 Data Link Connector Location
1 – HEADLAMP SWITCH
2 – DATA LINK CONNECTOR (LEFT SIDE OF COLUMN ABOVE
BRAKE PEDAL)
7 - 10
COOLING SYSTEM
WJ
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)