Isuzu Amigo / Axiom / Trooper / Rodeo / VehiCross. Manual - part 773
6E–116
TROOPER 6VE1 3.5L ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Fuel System Diagnosis
(Cont'd)
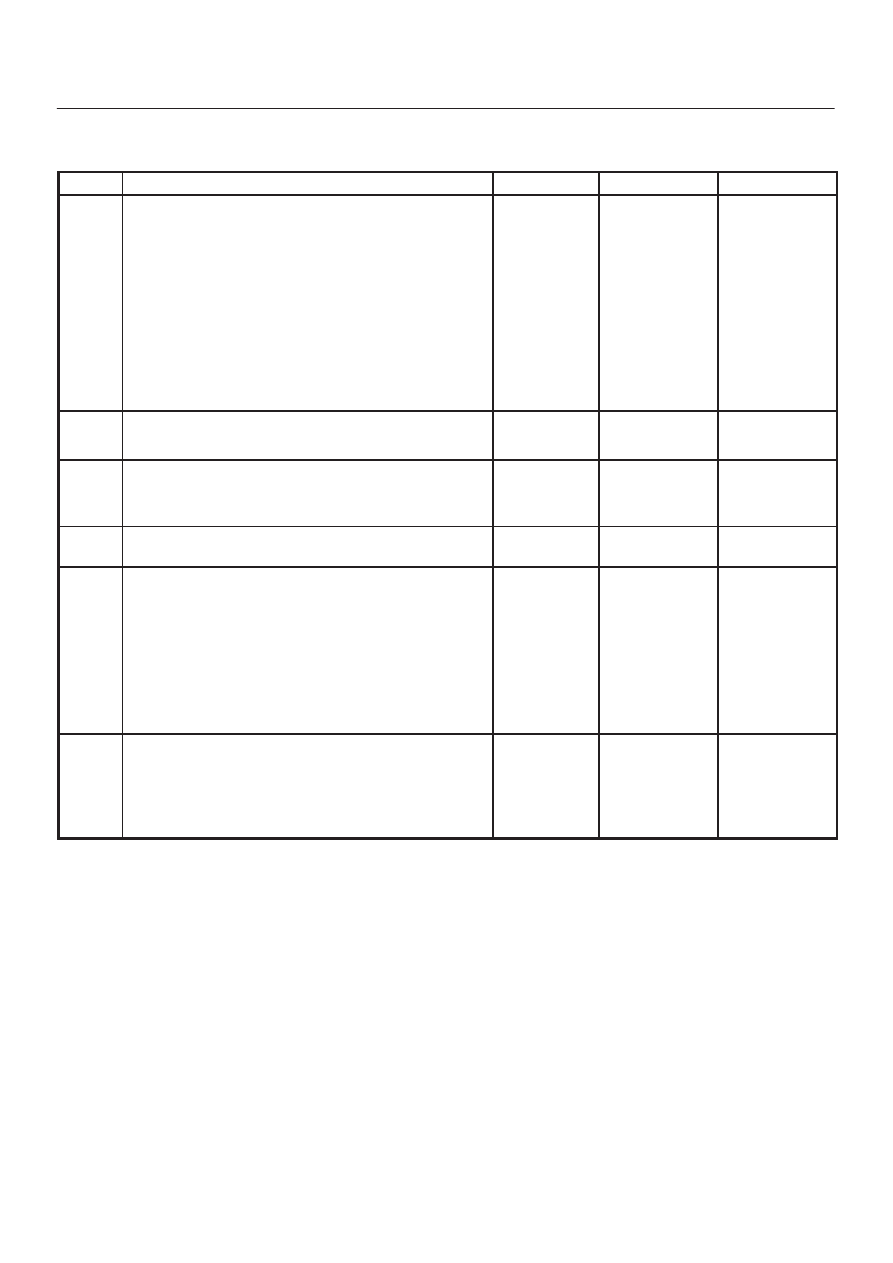
Step
No
Yes
Value(s)
Action
18
1. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to the
Fuel
Pressure Relief.
2. Disconnect the fuel return line from the fuel rail.
3. Attach a length of flexible hose to the fuel rail return
outlet passage.
4. Place the open end of the flexible hose into an
approved gasoline container.
5. Run the fuel pump with the Tech 2.
6. Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel
pressure gauge with the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits?
290-376 kPa
(42-55 psi)
Go to
Step 19
Go to
Step 20
19
Locate and correct the restriction in the fuel return line.
Is the action complete?
—
Verify repair
—
20
Visually and physically inspect the fuel rail outlet
passages for a restriction.
Was a restriction found?
—
Verify repair
Go to
Step 11
21
Is the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge above the specified value?
0 kPa (0 psi)
Go to
Step 22
Go to
Step 23
22
1. Command the fuel pump “ON” with the Tech 2.
2. Using suitable pliers which will not damage the fuel
hose, gradually apply pressure with the pliers to
pinch the flexible fuel return hose closed.
CAUTION: Do not let the fuel pressure exceed
the second specified value.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge rise above the first specified value?
376 kPa
(55 psi)
414 kPa
(60 psi)
Go to
Step 11
Go to
Step 7
23
1. Command the fuel pump “ON” with the Tech 2.
2. Remove the fuel filler cap and listen for the sound of
the fuel pump running.
3. Turn the pump off.
Was the fuel pump running?
—
Go to
Step 7
Go to
Fuel
System
Electrical Test
Chart