Isuzu KB P190. Manual - part 825
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
Page 6C1-2–22
5 Symptoms
Diagnostics
5.1
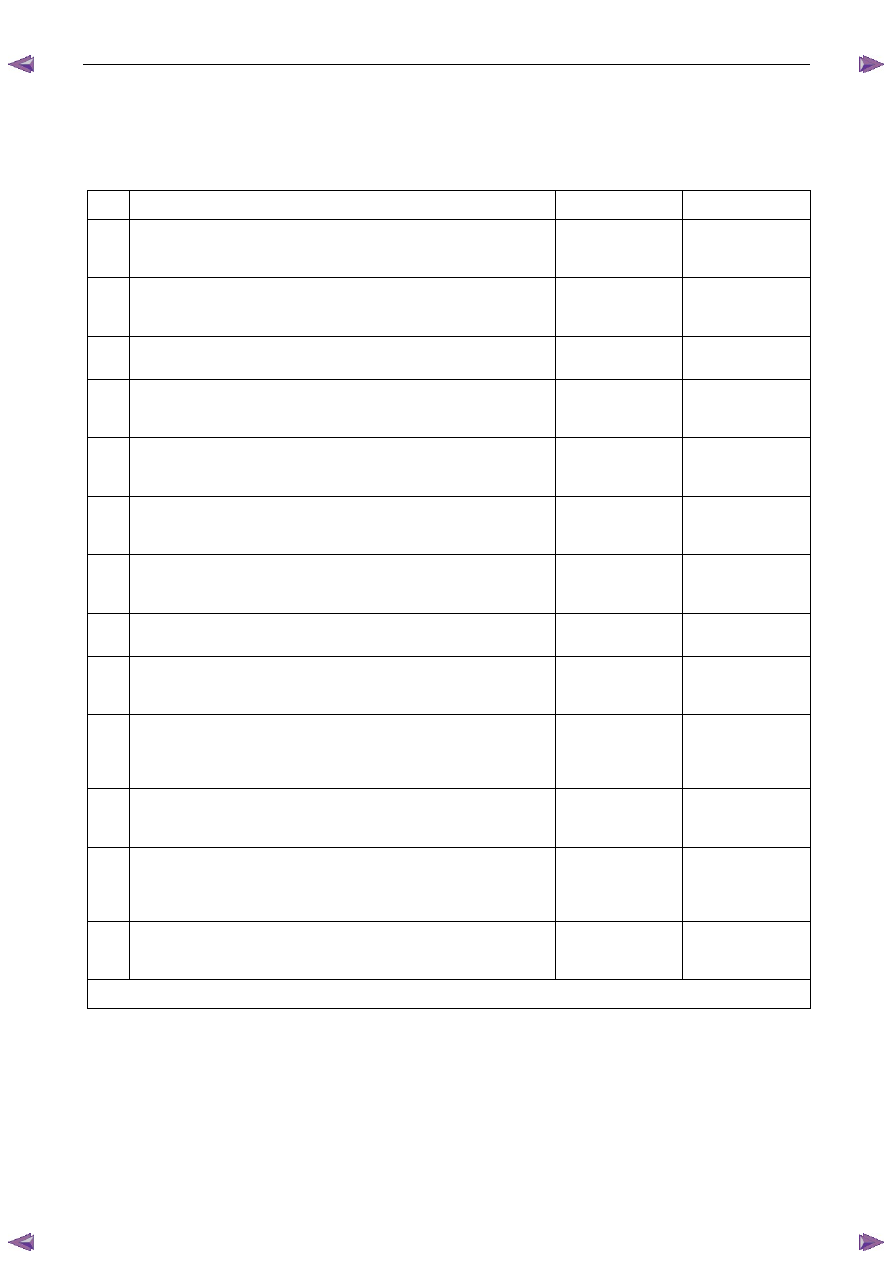
Symptoms Diagnosis Table
Step Action
Yes
No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2
Is the fault intermittent?
Refer to
5.2 Intermittent
Fault Conditions
Go to Step 3
3
Does the engine backfire?
Refer to
5.3 Backfire
Go to Step 4
4
Does the engine crank but does not run?
Refer to
5.4 Cranks
But
Does Not Run
Go to Step 5
5
Does the engine cut-out or miss?
Refer to
5.5 Cuts
Out,
Misses
Go to Step 6
6
Is there a detonation or spark knock noise coming from the engine?
Refer to
5.6 Detonation /
Spark Knock
Go to Step 7
7
Is there an engine dieseling or run-on condition?
Refer to
5.7 Dieseling,
Run-on
Go to Step 8
8
Is there an engine hard starting condition?
Refer to
5.8 Hard
Start
Go to Step 9
9
Is there an engine hesitation, sag or stumble condition?
Refer to
5.9 Hesitation,
Sag and Stumble
Go to Step 10
10 Does the engine suffer from lack of power, sluggishness or
sponginess?
Refer to
5.10 Lack of Power,
Sluggishness or
Sponginess
Go to Step 11
11 Does the engine suffer from poor fuel economy?
Refer to
5.11 Poor
Fuel
Economy
Go to Step 12
12 Does the engine suffer from rough, unstable or incorrect idle and
engine stalling?
Refer to
5.12 Rough,
Unstable, Incorrect
Idle or Stalling
Go to Step 13
13 Does the engine surge or chuggle?
Refer to
5.13 Surges
/
Chuggles
Go to Step 14
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.2
Intermittent Fault Conditions
Description
A fault condition is intermittent if one of the following conditions exists:
•
the fault condition is not always present,
•
the fault condition cannot be presently duplicated, or