Infiniti I35 (A33). Manual - part 9
SAT011J
OFF-time INCREASING
"
Amount of drain DECREASING
"
Pilot pressure HIGH
"
Lock-up RELEASING
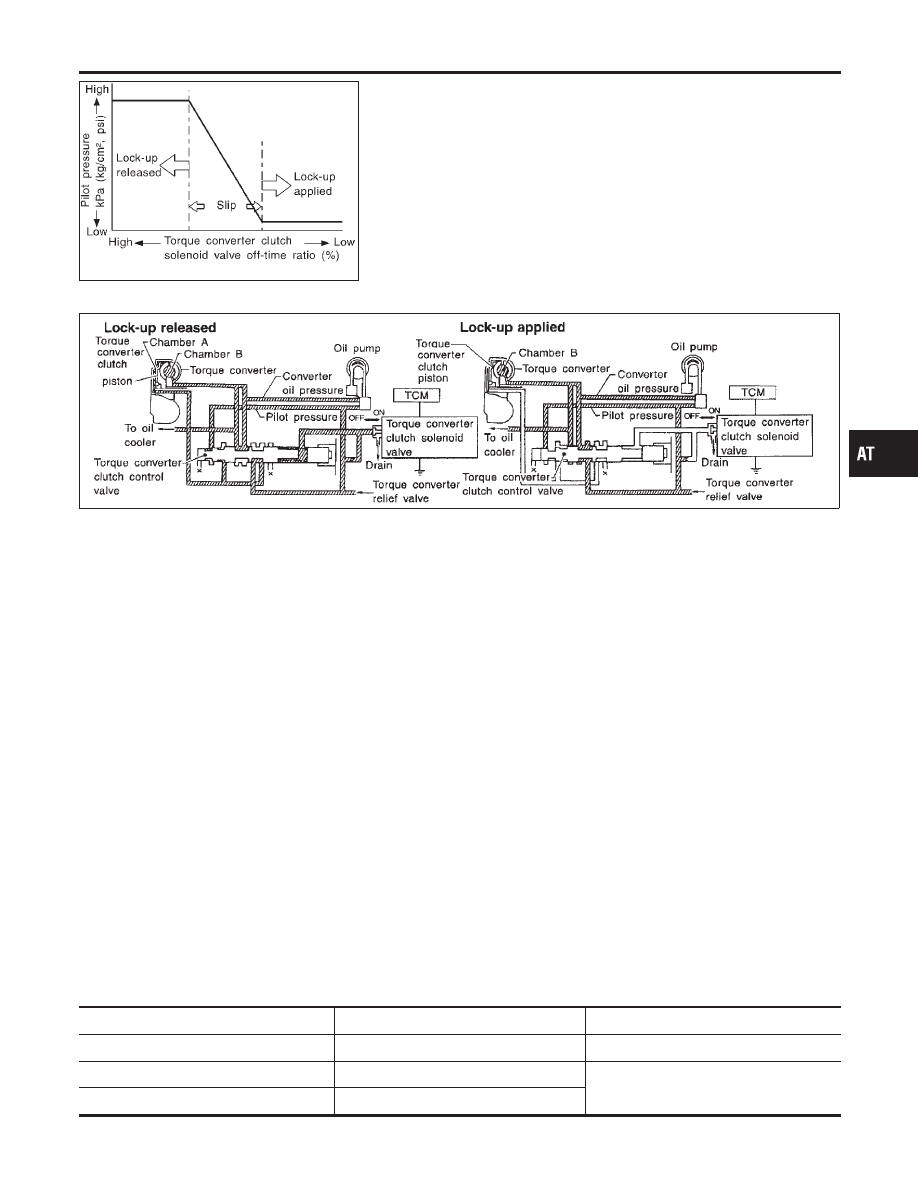
Torque Converter Clutch Control Valve Operation
NHAT0015S0303
AAT155A
Lock-up released
The OFF-duration of the torque converter clutch solenoid valve is
long, and pilot pressure is high. The pilot pressure pushes the end
face of the torque converter clutch control valve in combination with
spring force to move the valve to the left. As a result, converter
pressure is applied to chamber A (torque converter clutch piston
release side). Accordingly, the torque converter clutch piston
remains unlocked.
Lock-up applied
When the OFF-duration of the torque converter clutch solenoid
valve is short, pilot pressure drains and becomes low. Accordingly,
the control valve moves to the right by the pilot pressure of the
other circuit and converter pressure. As a result, converter pres-
sure is applied to chamber B, keeping the torque converter clutch
piston applied.
Also smooth lock-up is provided by transient application and
release of the lock-up.
OVERRUN CLUTCH CONTROL (ENGINE BRAKE
CONTROL)
NHAT0015S04
Forward one-way clutch is used to reduce shifting shocks in down-
shifting operations. This clutch transmits engine torque to the
wheels. However, drive force from the wheels is not transmitted to
the engine because the one-way clutch rotates idle. This means the
engine brake is not effective.
The overrun clutch operates when the engine brake is needed.
Overrun Clutch Operating Conditions
NHAT0015S0401
Selector lever position
Gear position
Throttle opening
D position
D
1
, D
2
, D
3
gear position
Less than 3.0/16
2nd position
2
1
, 2
2
gear position
At any position
1st position
1
1
, 1
2
gear position
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
OVERALL SYSTEM
Control Mechanism (Cont’d)
AT-33