Daewoo Musso. Manual - part 202
2A-2 SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS
Application
Description
4.75 - 5.25
Power Voltage (V)
Axle Vertical
Acceleration
Sensor
(Wheel G
Sensor)
Less than 10
Consuming Current (mA)
Less than 2.0
Output Current (mA)
Operating Characteristics
Type
Damping
Force
Switching
Actuator
3-stage Rotary Step Motor Type
Voltage Rating (V)
DC12
Current Rating (A)
Less than 2.5
Current Time (mS)
95 - 105
4.75 - 5.25
Power Voltage (V)
Body
Vertical and
Lateral
Acceleration
Sensor
Less than 10
Consuming Current (mA)
Less than 2.0
Output Current (mA)
Operating Characteristics
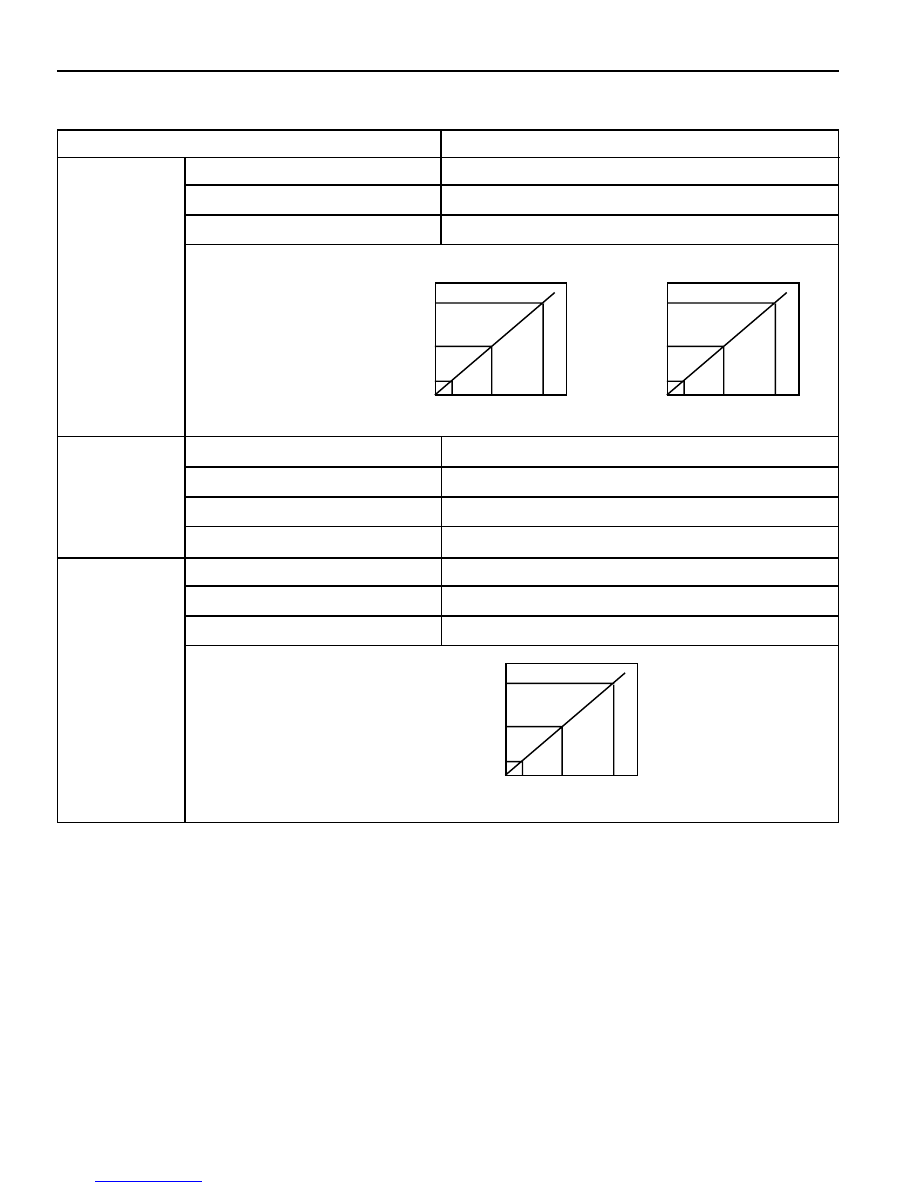
Output Voltage
0.75
2.5
4.25
-1.5g
1g
3.5g
Acceleration
(Vertical Acceleration Sensor)
Output Voltage
0.75
2.5
4.25
-1g
0g
1g
Acceleration
(Lateral Acceleration Sensor)
Output Voltage
0.75
2.5
4.25
-9g
1g
11g
Acceleration
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS (Cont'd)