Nissan Murano Z50 (2006 year). Manual - part 136
GI-30
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 August
2006 Murano
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
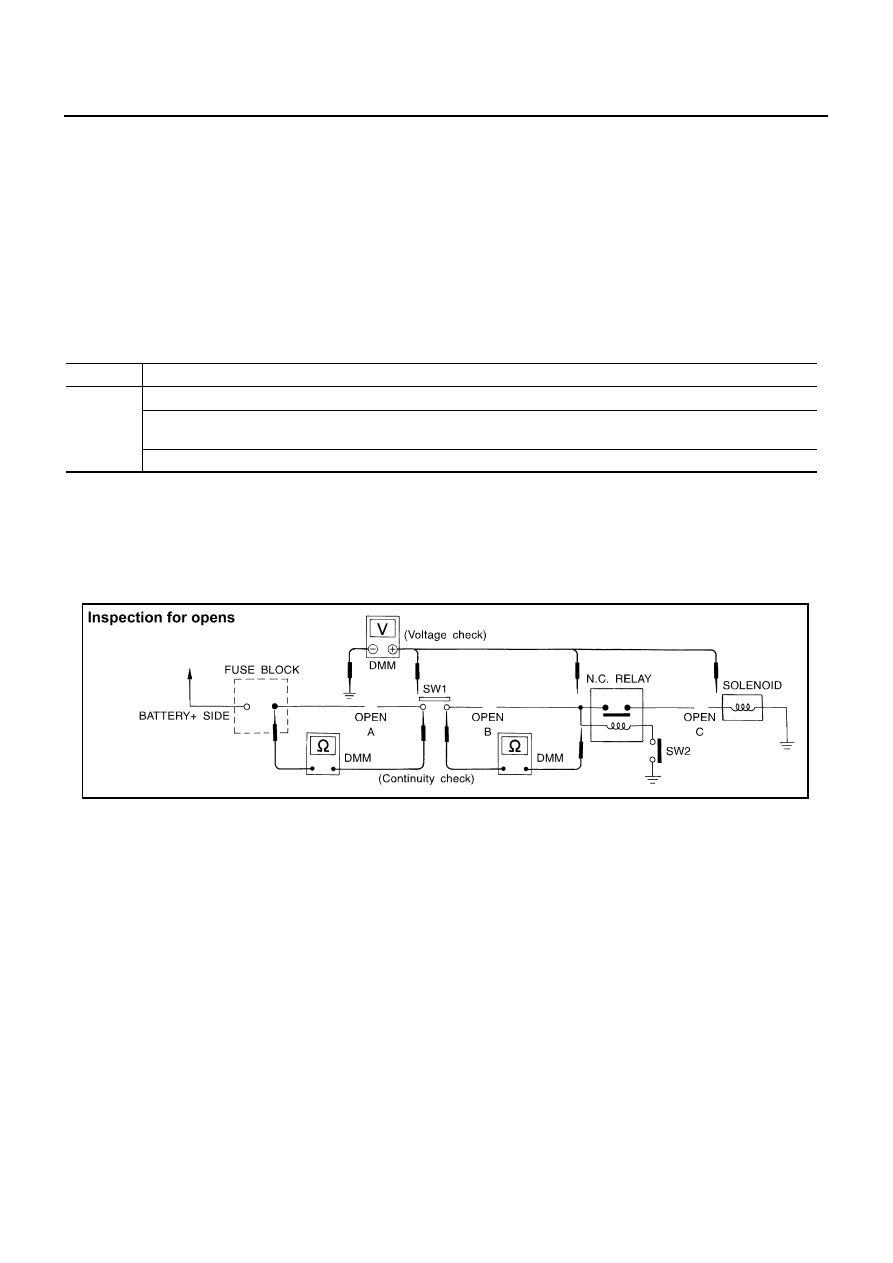
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
●
Disconnect the battery negative cable.
●
Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
●
Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
●
Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
●
Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
●
Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPEN
A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORT
There are two types of shorts.
●
SHORT CIRCUIT
When a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
●
SHORT TO GROUND
When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A