Mazda X-5. Manual - part 39
CONTROL SYSTEM
01–40–29
01–40
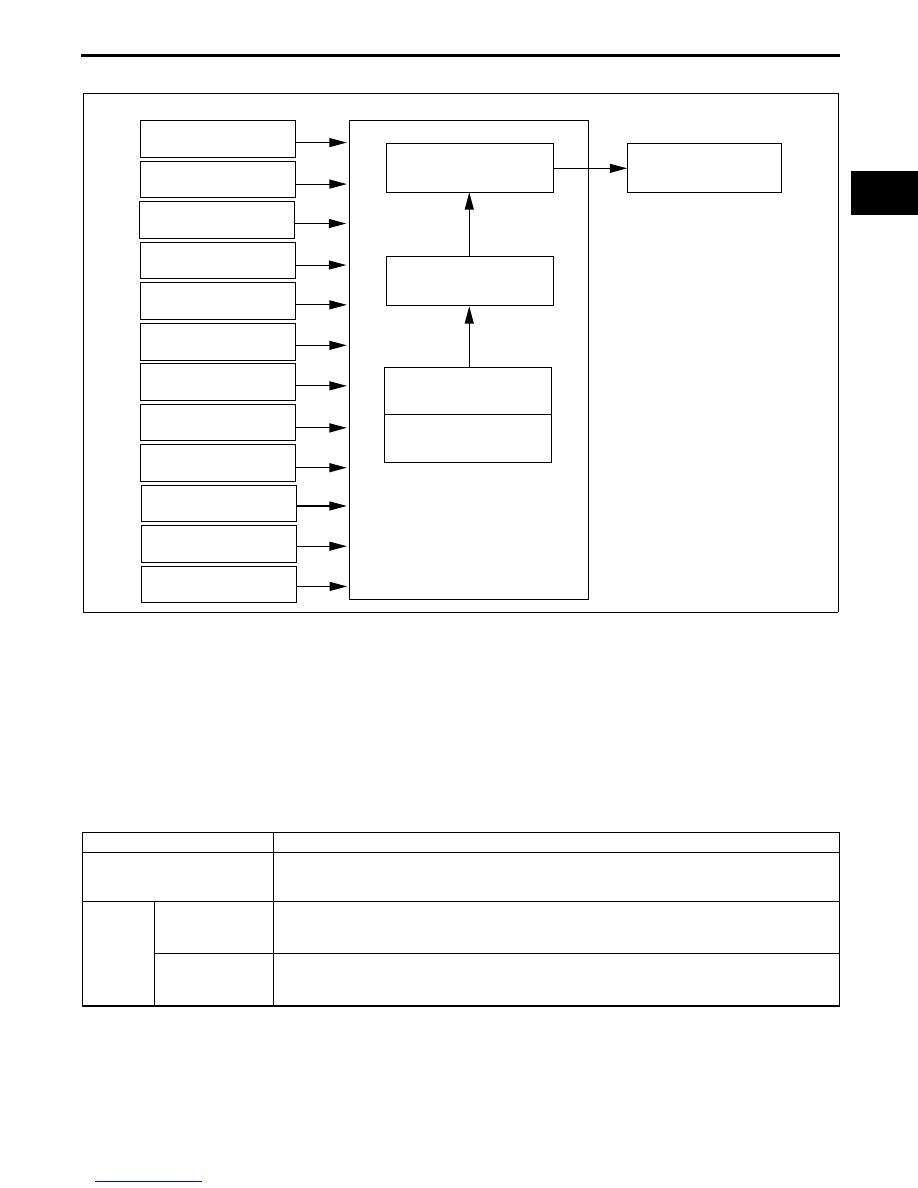
EVAPORATIVE PURGE CONTROL BLOCK DIAGRAM [LF]
E5U014000000N38
End Of Sie
EVAPORATIVE PURGE CONTROL OPERATION [LF]
E5U014000000N39
Determination of Purge Solenoid Valve Energization Time
• The PCM determines the target purge flow amount according to engine operation conditions as the basic flow
amount. The actual operation delays the build-up of operation current from coil inductance and corrects
energization time according to fluctuation in battery voltage to cause operation delay based on the mass of the
needle valve and plunger, and spring resistance. The lower the rate of battery positive voltage, the longer the
energization time.
Calculation Method for Purge Flow Amount
• The PCM determines the purge flow amount through the addition of each correction to the basic purge flow
amount.
Operation Conditions
• For purge control during normal driving, the PCM sends a duty signal to the purge solenoid valve when all of
the following conditions are met.
— Fuel injection control is in the feedback zone or the high load volume increase zone.
— Airflow passage damage related DTC is not stored.
— Engine coolant temperature is 70
°C {158 °F} or more.
End Of Sie
MAF SENSOR
IAT SENSOR
MAP SENSOR
CKP SENSOR
BARO SENSOR
FRONT HO2S
BATTERY
NEUTRAL SWITCH (MT)
TR SWITCH (AT)
PURGE SOLENOID VALVE
ENERGIZATION TIME
PURGE FLOW AMOUNT
BASIC PURGE FLOW
AMOUNT
CORRECTIONS
PURGE SOLENOID
VALVE
PCM
TP SENSOR NO.1, NO.2
ECT SENSOR
BRAKE SWITCH
NO.1, NO.2
E5U140ZT5007
Contents
Calculation or determination method of purge flow amount and correction
Basic purge flow amount
The basic purge flow amount is determined by multiplying the intake air temperature
correction to the purge mass volume which is calculated by multiplying the base purge rate
and the intake air mass volume, which differs according to engine conditions.
Correction
Purge startup
correction
Purpose: Prevents a sudden change in air/fuel ratio during the startup of purge control.
During purge control startup
• When purge control operation conditions are met→correction
Volume decrease
correction
Purpose: Decreases the amount of purge flow and stabilize the air/fuel ratio.
When the fuel injection control feedback correction value is unstable
• According to the front HO2S feedback condition