Mazda X-5. Manual - part 36
CONTROL SYSTEM
01–40–17
01–40
Maximum Cam Retard Mode
Mode execution condition
• When any of the following conditions are met:
— Cranking
— Idling after completion of cleaning mode
— DTC stored for the following devices:
• ECT sensor
• CKP sensor
• CMP sensor
• TP sensor
• MAF sensor
• OCV
Purpose
• Maximum cam retard mode stabilizes engine speed by maximally retarding the valve timing when the engine
speed is low during idling.
Operation
• When the target current in the maximum cam retard mode is fixed at 100 mA. When 100 mA current is
supplied, the OCV opens the hydraulic passage for the retard chamber and hydraulic pressure from the oil
pump is introduced to the retard chamber. Because of this, the variable valve timing actuator is fixed at the
maximum retard position (minimum overlap).
Feedback Hold Mode
Mode execution condition
• Target valve timing and actual valve timing are almost the same.
Purpose
• The feedback hold mode holds the valve timing by returning the OCV spool valve to the neutral position when
target valve timing suitable for the engine operation conditions is obtained.
Operation
• Though the target current in the feedback hold mode is basically around 600 mA, feedback operation is
performed at all times so that the present OCV drive current approaches the target current. Because the hold
current changes due to mechanical variation between engines and deterioration due to aging on OCV internal
parts, the PCM continues to learn the changing current (hold current learning value) to maintain the spool valve
in the neutral position.
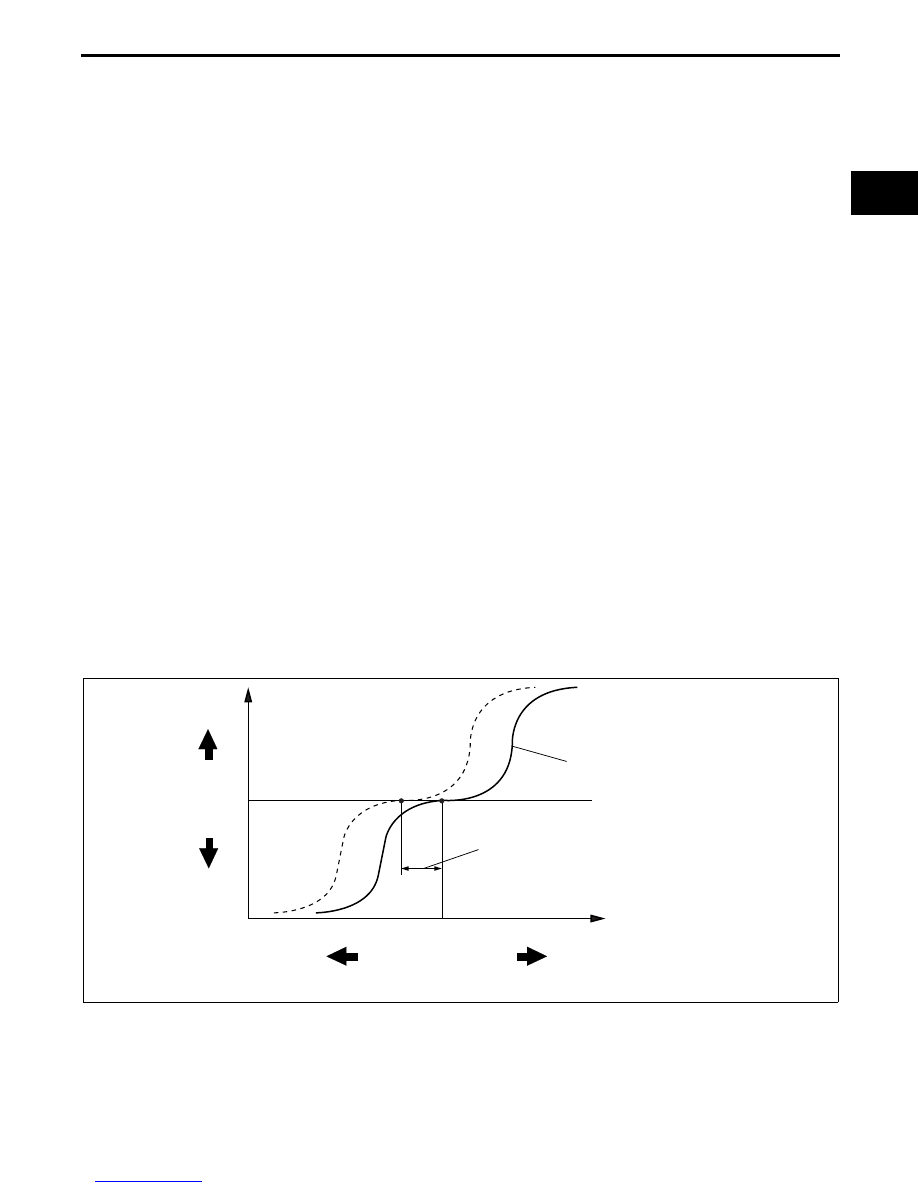
ADVANCE SPEED INCREASES
AS INCLINATION INCREASES
CHANGES ACCORDING TO MECHANICAL
VARIANCE AND AGED DETERIORATION
ADVANCE
RETARD
APPROX. 100 mA
APPROX. 600 mA
APPROX. 1,000 mA
OCV OPERATION CURRENT
E5U140ZT5101