Mazda X-5. Manual - part 35
CONTROL SYSTEM
01–40–13
01–40
DRIVE-BY-WIRE CONTROL OPERATION [LF]
E5U014000000N60
Idle Speed Control
• Controls the throttle valve opening angle so that it is close to the target idle speed calculated by the PCM.
• The PCM calculates the target throttle opening angle by adding each type of correction to the basic duty value
which is the basis of the throttle valve opening angle, and then sends a duty signal to the throttle valve actuator.
The basic duty value is determined by the target engine speed.
• Each type of correction is as follows.
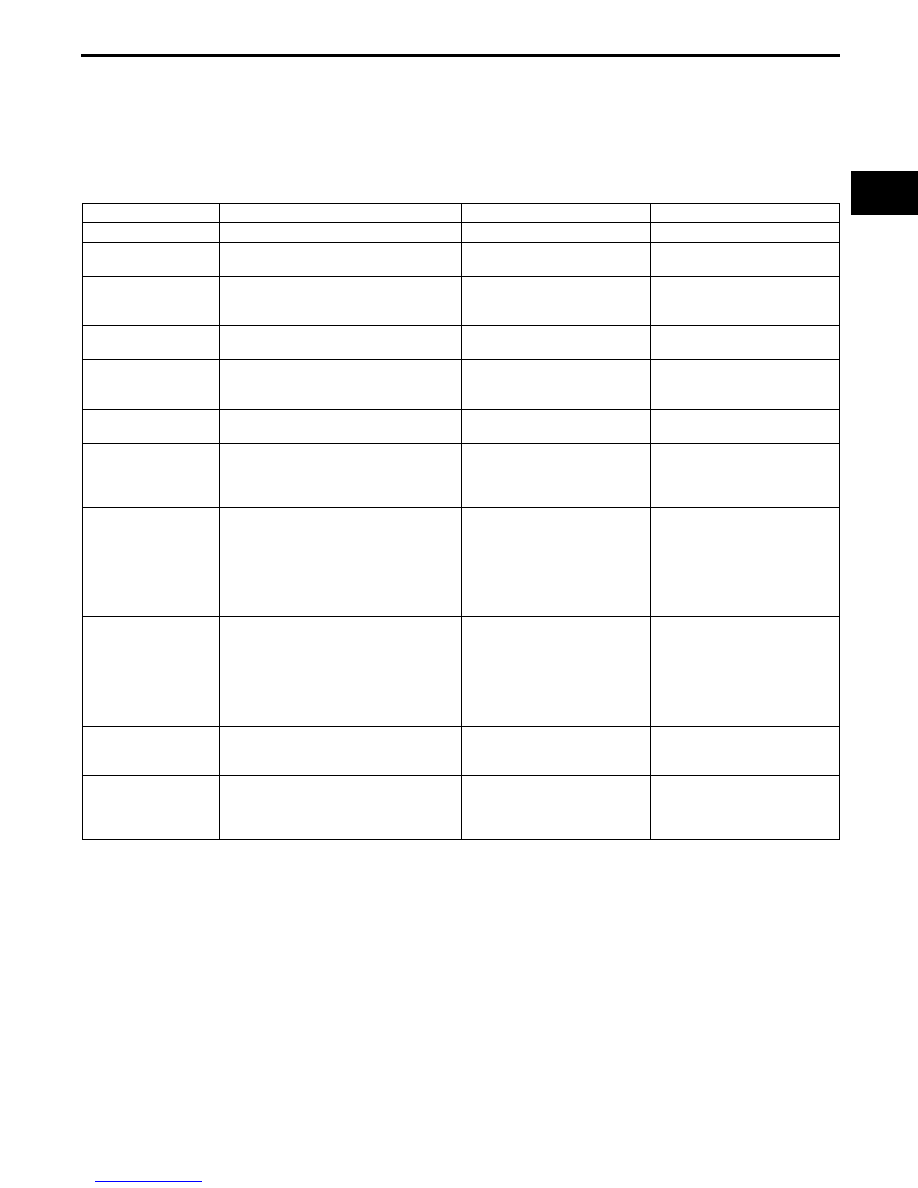
Correction
Accelerator Control
• Controls the throttle valve opening angle through control of the throttle valve actuator, according to the amount
of AP depression.
• The PCM controls the throttle valve actuator so that the actual throttle valve opening angle is close to the target
throttle valve opening angle.
• The final throttle valve opening angle is determined by the sum of the target throttle opening angle during idling
and the target throttle valve opening angle during regular driving.
• The target throttle valve opening angle during regular driving is determined based on the transmission gear
position, the amount of AP depression and the engine speed. If the target throttle opening angle is at the fixed
value or less during regular driving, the PCM switches to idle speed control.
• The PCM sets the throttle valve to the fully-closed position when the ignition switch is on or off and executes the
idle position learning function to learn the throttle valve position. Due to this, changes in the throttle valve
opening angle due to age deterioration are corrected.
• When the ignition switch is off, a main relay on request is output and the fully-closed learning function is
executed. (See 01–40–11 MAIN RELAY CONTROL OPERATION [LF].)
Correction
Purpose
Condition
Amount of Correction
Correction
Target
Conditions
Correction amount
A/C load correction
Prevents decrease in idle speed due to
A/C operation.
A/C is operating.
A/C operation
time
→correction
Electrical load
correction
Prevents decrease in idle speed due to
electrical load operation.
Idle speed during electrical
load operation and under any
condition during driving
High electrical load
→large
correction
D-range correction
(AT)
Prevents decrease in idle speed due to
shifting into D-range
D-range signal is input.
Low idle speed when shifted
to D range
→large correction
Dashpot correction
Prevents decrease in idle speed due to
insufficient intake air amount during
deceleration.
Decelerated
High engine speed
→large
correction
Correction at engine
start
Prevents decrease in idle speed after
engine start.
After cranking and engine
start
Low ECT
→large correction
Hot engine restart
correction
Prevents decrease in idle speed from
hot engine restart.
Just after cranking and engine
start when the ECT is 60
°C
{140
°F} or more the IAT is 50
°C {122 °F} or more
High intake airflow
temperature
→large correction
Feedback correction
A
Sets idle speed to target engine speed. Idle speed during idling
(vehicle is stopped) is over or
under the target engine speed
(except during test mode
when the engine speed is 300
rpm or less).
Actual idle speed
Target engine speed or
less
→volume increase
correction
Target engine speed or
more
→volume decrease
correction
Feedback correction
B
Sets to the target engine speed when
the idle speed has decreased in the
range not corrected by feedback
correction A, and prevents a decrease
in idle speed.
During deceleration at fully
closed throttle, the engine
speed is the target engine
speed or more and when the
feedback correction A is not
performed (except during test
mode).
Large difference between
actual idle speed and target
engine speed
→large
correction
Engaged coasting
clutch volume
increase correction
Reduces shock when the transaxle
coasting clutch is engaged.
When coasting clutch is
engaged.
High vehicle speed
→large
correction
Learning correction
Stores intake air volume changes
based on differences between engines
and changes due to aged deterioration,
and feedback.
During feedback correction A
when ECT is 85
°C {185 °F} or
more.
During idling
→average value
of feedback correction A