Mazda X-5. Manual - part 8
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC
01–02–9
01–02
*1
: California emission regulation applicable model
*2
: MT
*3
: C: CMDTC self-test, O: KOEO self-test, R: KOER self-test
*4
: With ABS/DSC or MT without ABS/DSC
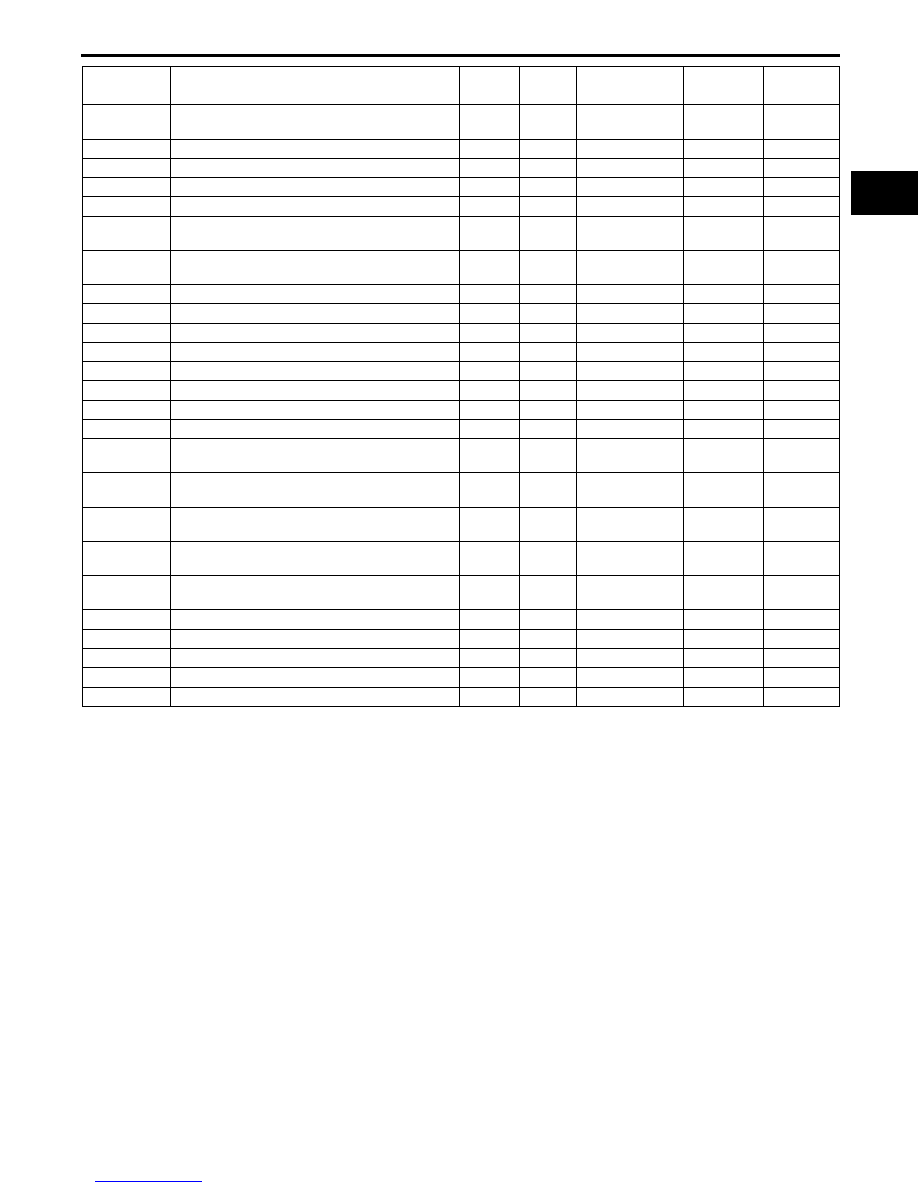
P2119
Throttle actuator control throttle body range/
performance problem
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2122
APP sensor No.1 circuit low input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2123
APP sensor No.1 circuit high input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2127
APP sensor No.2 circuit low input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2128
APP sensor No.2 circuit high input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2135
TP sensor No.1/No.2 voltage correlation
problem
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2138
APP sensor No.1/No.2 voltage correlation
problem
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2177
Fuel system too lean at off idle
ON
2
Fuel system
C, R
×
P2178
Fuel system too rich at off idle
ON
2
Fuel system
C, R
×
P2187
Fuel system too lean at idle
ON
2
Fuel system
C, R
×
P2188
Fuel system too rich at idle
ON
2
Fuel system
C, R
×
P2195
Front HO2S signal stuck lean
ON
2
HO2S
C
×
P2196
Front HO2S signal stuck rich
ON
2
HO2S
C
×
P2228
BARO sensor circuit low input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2229
BARO sensor circuit high input
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2401
EVAP system leak detection pump motor
circuit low
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2402
EVAP system leak detection pump motor
circuit high
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2404
EVAP system leak detection pump sense
circuit problem
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2405
EVAP system leak detection pump sense
circuit low input
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2407
EVAP system leak detection pump sense
circuit intermittent
ON
2
CCM
C, R
×
P2502
Charging system voltage problem
OFF
1
Other
C, R
×
P2503
Charging system voltage low
OFF
1
Other
C, R
×
P2504
Charging system voltage high
OFF
1
Other
C, R
×
P2507
PCM B+ voltage low
ON
1
CCM
C, O, R
×
P2610
PCM internal engine off timer performance
ON
2
CCM
C
×
DTC No.
Condition
MIL
DC
Monitor item
Self-test
type*
3
Memory
function