Range Rover 2. Electrical Manual - part 9
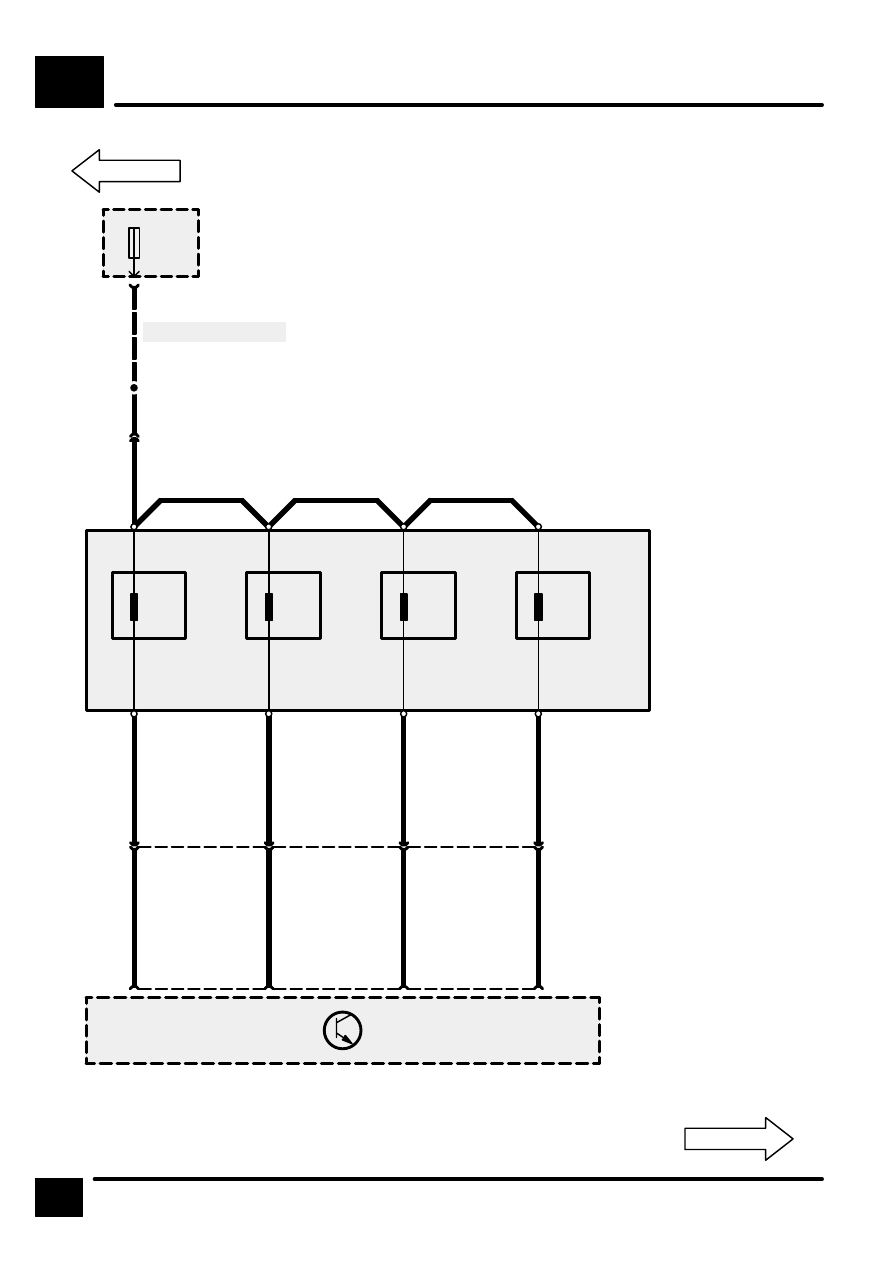
SEQUENTIAL MULTIPORT FUEL INJECTION (SFI–V8)
A1
16
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
C509
13
14
Z132
Engine Control
Module (ECM)
S509
Z261
Ignition Coils
15
1
3
2
4
C525
1
1&6
2&3
4&7
5&8
5
C525
W
See Fuse Details
P125a
Engine Compart-
ment Fuse Box
15
F 26
20 A
WB
WU
WY
WK
R
R
R
R
U
O
P
G
C508
8