Range Rover Body Repair Manual - part 45
77
PANEL REPAIRS
NEW RANGE ROVER
6
PANELS
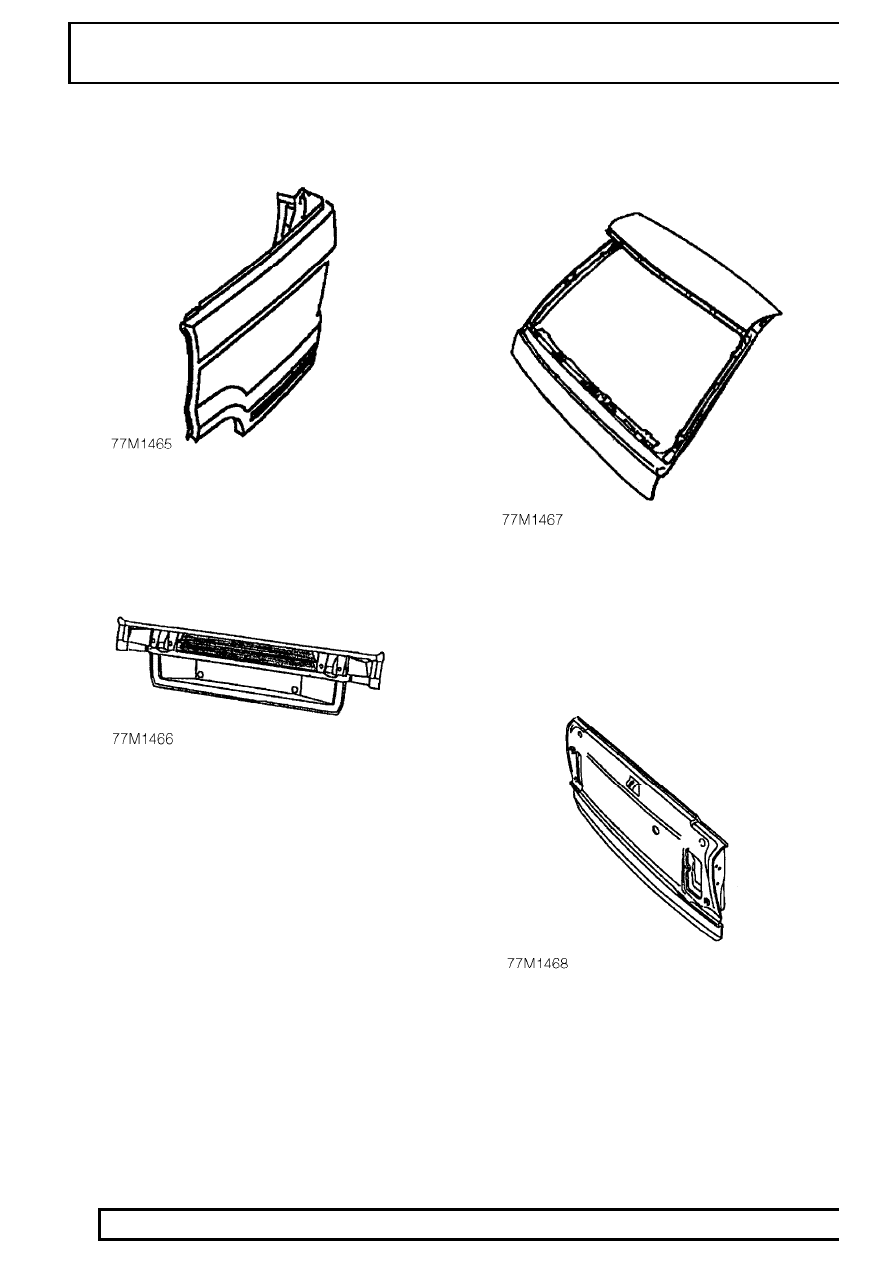
Outer Rear Quarter Panel
Outer rear quarters are serviced as a separate panel.
Lower Panel
Lower panels are serviced as an assembly including
the tailgate lock reinforcement.
Upper Tailgate Assembly
Upper tailgates are serviced less hinges, which are
available separately.
Lower Tailgate Assembly
Lower tailgate assemblies comprise an aluminium
outer panel fitted to a steel frame and are serviced
less hinges, which are available separately. Lower
tailgate outer panels are also serviced as separate
items.