Frelander 2. Manual - part 197
Item
Part Number
Description
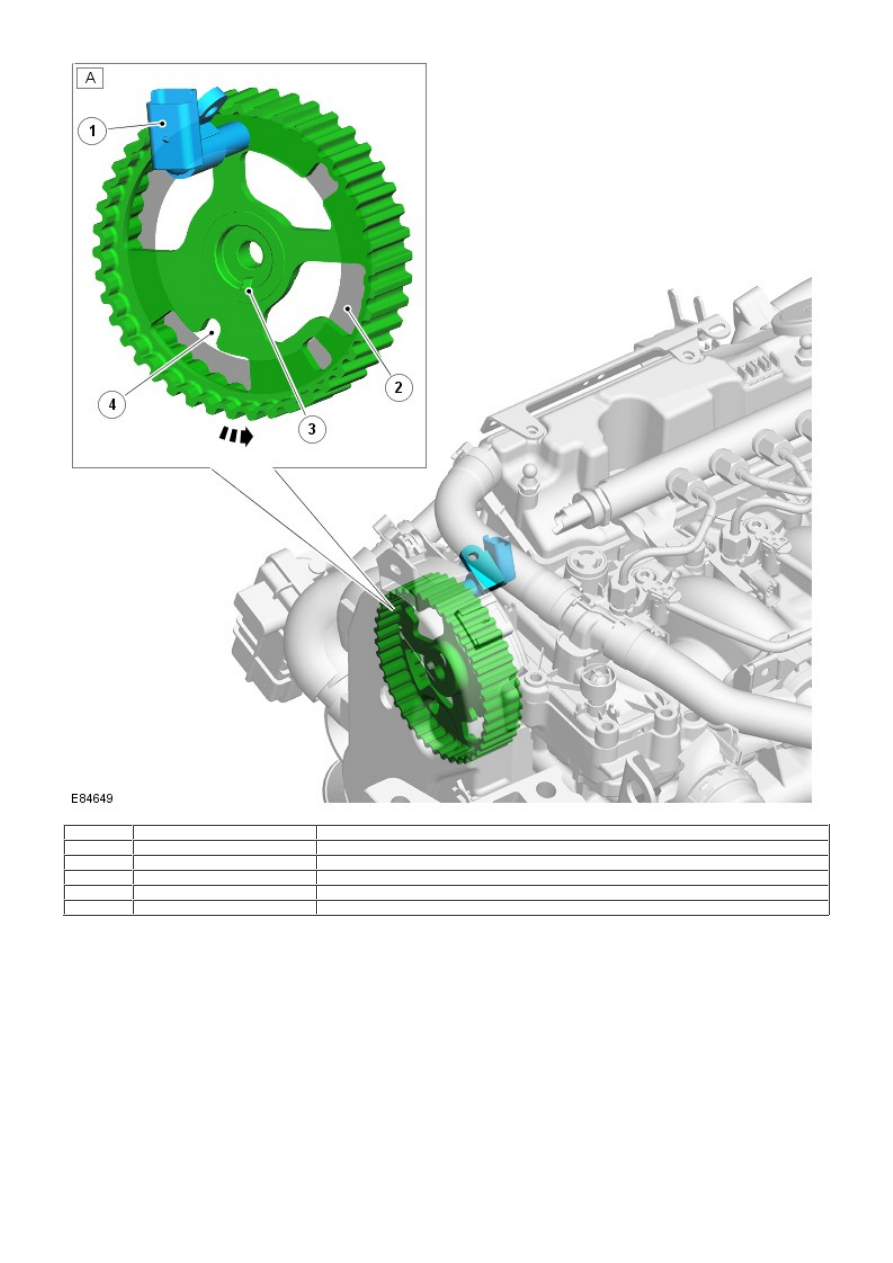
A
-
Rear view of exhaust camshaft pulley
1
-
CMP sensor
2
-
CMP target area
3
-
Camshaft pulley key slot
4
-
Camshaft timing pin location
The CMP sensor is mounted at the front of the engine behind the exhaust camshaft drive pulley. The sensor tip protrudes
through a hole in the cylinder head cover, and is positioned close to the camshaft pulley target area. The position of the
sensor to the camshaft pulley is adjustable.
For further details on setting the CMP sensor gap, refer to the relevant Service Repair Procedures (SRP) manual.
The sensor is a variable reluctance sensor that provides a signal of No. 1 cylinder camshaft position to the ECM. The
information is used by the ECM to determine the precise moment for injection during engine cranking.
For additional information, refer to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14 Electronic Engine Controls - 2.2L Duratorq - Td4,
Description and Operation).
Intake and Exhaust Valves