Jeep XJ. Manual - part 156
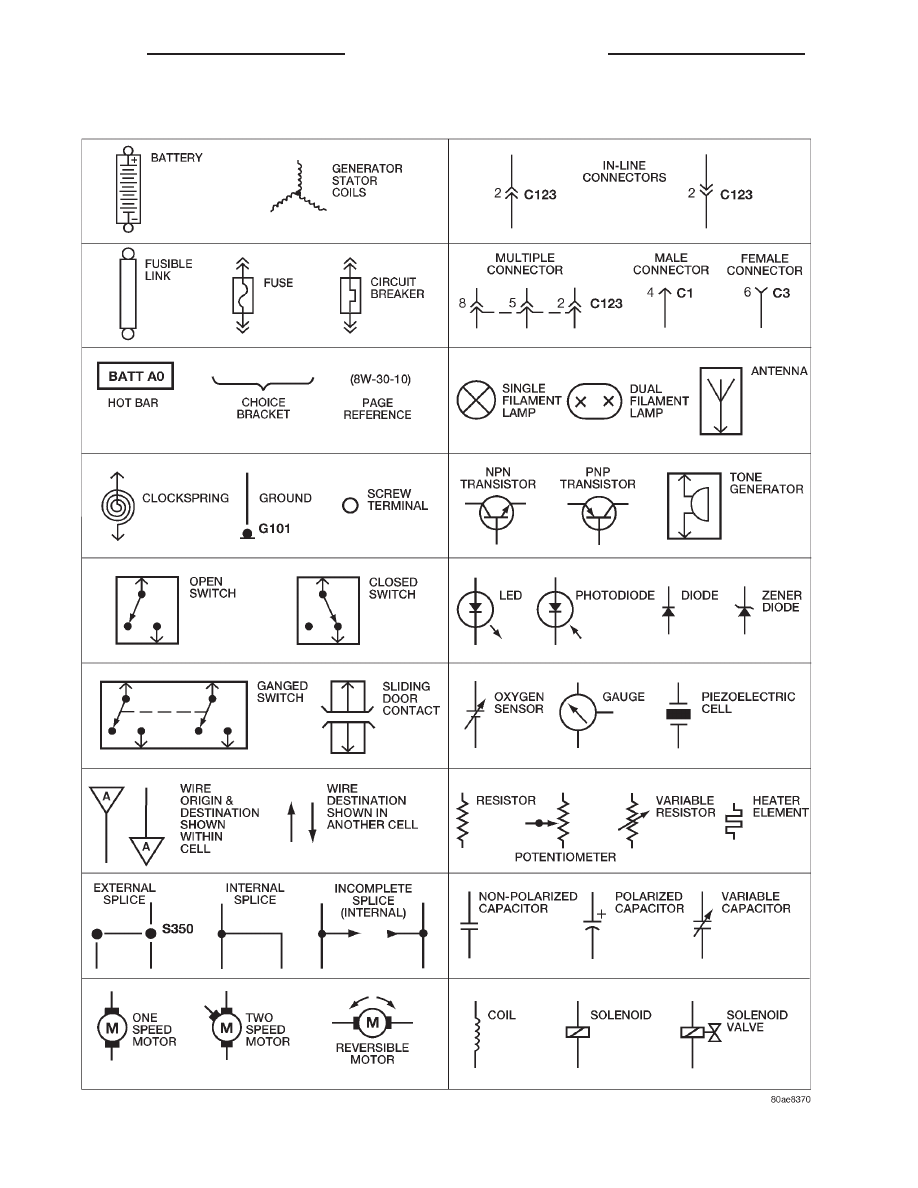
Wiring Diagram Symbols
8W - 01 - 6
8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION
XJ
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
|
|
|

Wiring Diagram Symbols 8W - 01 - 6 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION XJ DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued) |