Jeep XJ. Manual - part 86
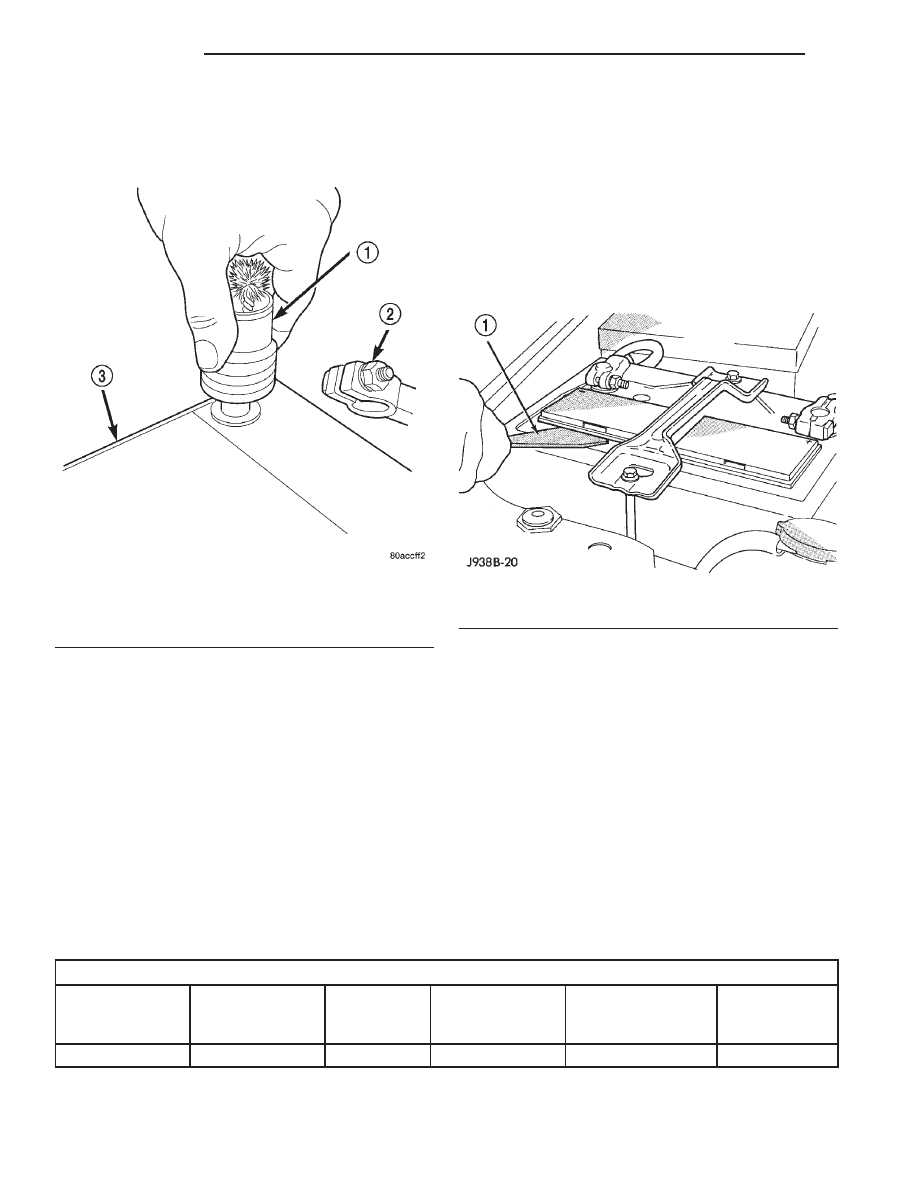
(5) Clean any corrosion from the battery terminal
posts with a wire brush or a post and terminal
cleaner, and a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution (Fig. 26).
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp.
(2) Inspect the battery tray and battery hold down
hardware for damage. Replace any damaged parts.
(3) Slide the thermoguard off of the battery case.
Inspect the battery case for cracks or other damage
that could result in electrolyte leaks. Also, check the
battery terminal posts for looseness. Batteries with
damaged cases or loose terminal posts must be
replaced.
(4) Inspect the battery thermoguard for tears,
cracks, deformation or other damage. Replace any
battery thermoguard that has been damaged.
(5) Inspect the electrolyte level in the battery. Use
a putty knife or another suitable wide flat-bladed tool
to pry the cell caps off (Fig. 27). Do not use a screw-
driver. Add distilled water to each cell until the liq-
uid reaches the bottom of the vent well. DO NOT
OVERFILL.
(6) Inspect the battery built-in test indicator sight
glass for an indication of the battery condition. If the
battery is discharged, charge as required. Refer to
Battery in the index of this service manual for the
location of the proper battery diagnosis and testing
procedures for more information on the use of the
battery built-in test indicator. Also refer to Battery
Charging in the index of this service manual for the
location of the proper battery charging procedures.
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY
Battery Classifications and Ratings
Part Number
BCI Group Size
Classification
Cold
Cranking
Amperage
Reserve
Capacity
Ampere-Hours
Load Test
Amperage
56041105AB
34
500
110 Minutes
60
250
Fig. 26 Clean Battery Terminal Post - Typical
1 – TERMINAL BRUSH
2 – BATTERY CABLE
3 – BATTERY
Fig. 27 Removing Battery Cell Caps - Typical
1 – PUTTY KNIFE
8A - 24
BATTERY
XJ
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)