Jeep Wrangler TJ. Manual - part 451
INSTALLATION
The front mounts support the engine at each side.
These supports are made of resilient rubber.
(1) If the engine support bracket was removed,
position the bracket onto the block and install the
attaching bolts (Fig. 74) (Fig. 75). Tighten the bolts
to 50 N·m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Place the insulator on the support bracket.
Install
the
insulator
retaining
bolts
and
nuts.
Tighten the bolts and nuts to 40 N·m (30 ft. lbs)
torque.
(3) Install the through bolt and the retaining nut.
Tighten the through bolt nut to 48 N·m (35 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Remove the engine support.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL
A resilient rubber cushion supports the transmis-
sion at the rear between the transmission extension
housing and the rear support crossmember or skid
plate.
ALL TRANSMISSIONS
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle and support the transmission.
(3) Remove the nuts holding the support cushion
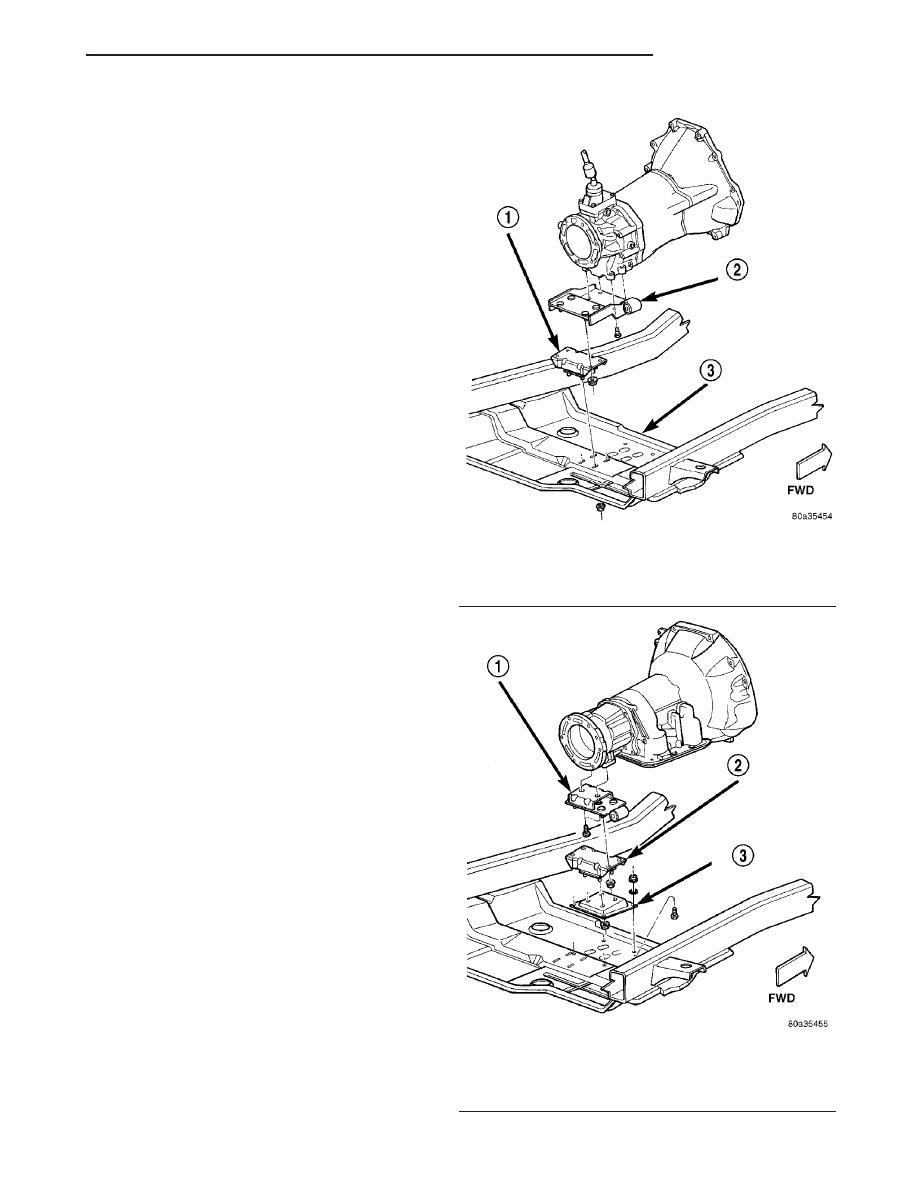
to the skid plate (Fig. 76) (Fig. 77).
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
(1) Remove nuts holding support cushion to trans-
mission support bracket.
(2) Remove the support cushion.
(3) Remove bolts holding transmission support
bracket to transmission.
(4) Remove the transmission support bracket.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
(1) Remove nuts holding support cushion to trans-
mission support bracket (Fig. 77). Remove the sup-
port cushion.
(2) Remove the bolts holding the transmission sup-
port bracket to transmission.
(3) Remove the transmission support bracket.
INSTALLATION
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
(1) Position the transmission mount bracket to the
transmission and install the bolts (Fig. 76).
(2) Tighten the bolts to 54 N·m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 76 Rear Mount (Manual Transmission)
1 - CUSHION
2 - BRACKET
3 - SKID PLATE
Fig. 77 Rear Mount (AutomaticTransmission)
1 - BRACKET
2 - CUSHION
3 - BRACKET
TJ
ENGINE 4.0L
9 - 119
FRONT MOUNT (Continued)