Jeep Liberty KJ. Manual - part 897
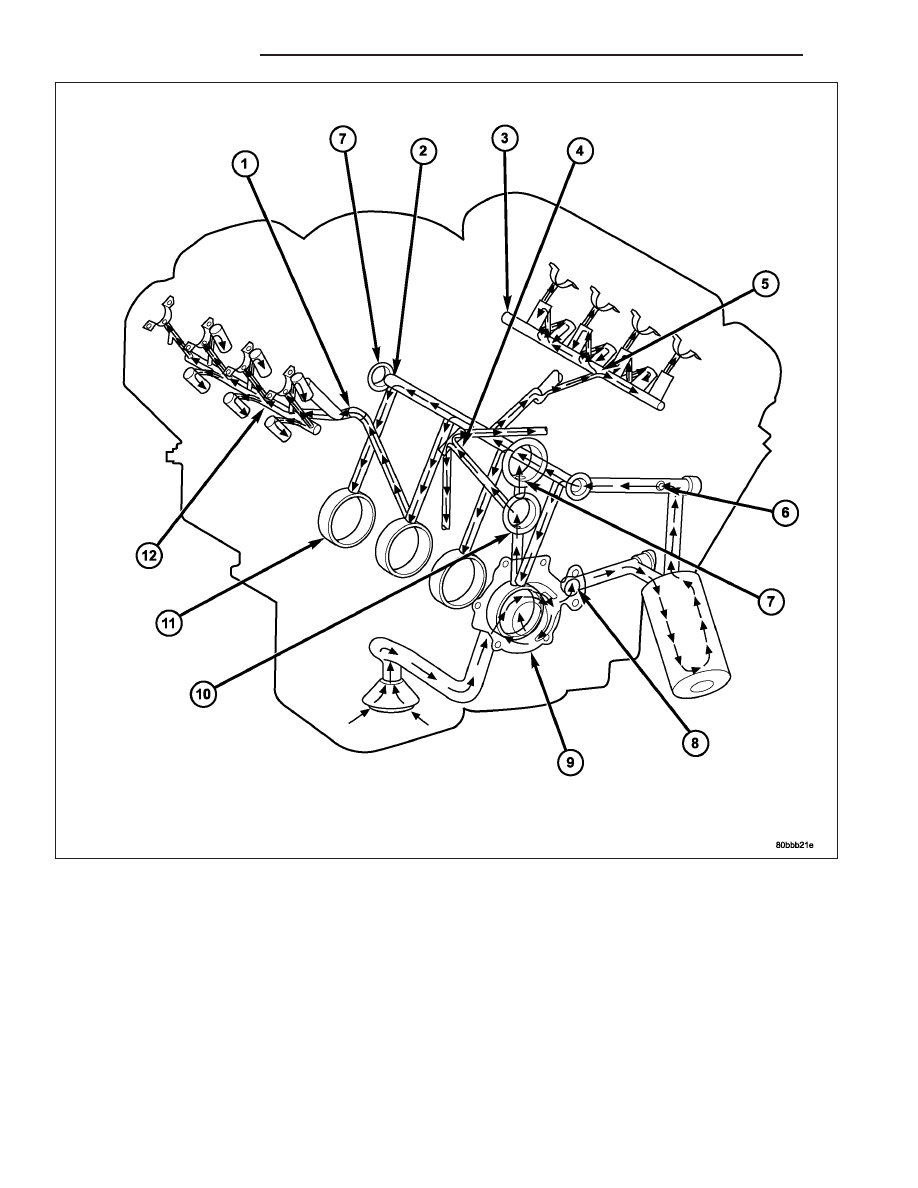
Oil from the oil pan is pumped by a gerotor type oil pump (9) directly mounted to the crankshaft nose. Oil pressure
is controlled by a relief valve mounted inside the oil pump housing.
The camshaft exhaust valve lobes and rocker arms are lubricated through a small hole in the rocker arm; oil flows
through the lash adjuster then through the rocker arm and onto the camshaft lobe. Due to the orientation of the
rocker arm, the camshaft intake lobes are not lubed in the same manner as the exhaust lobes. The intake lobes are
lubed through internal passages in the camshaft. Oil flows through a bore in the No. 3 camshaft bearing bore, and
as the camshaft turns, a hole in the camshaft aligns with the hole in the camshaft bore allowing engine oil to enter
the camshaft tube. The oil then exits through 1.6mm (0.063 in.) holes drilled into the intake lobes, lubricating the
lobes and the rocker arms.
9 - 1546
ENGINE - 3.7L
KJ