Content .. 1406 1407 1408 1409 ..
Jeep Liberty KJ. Manual - part 1408
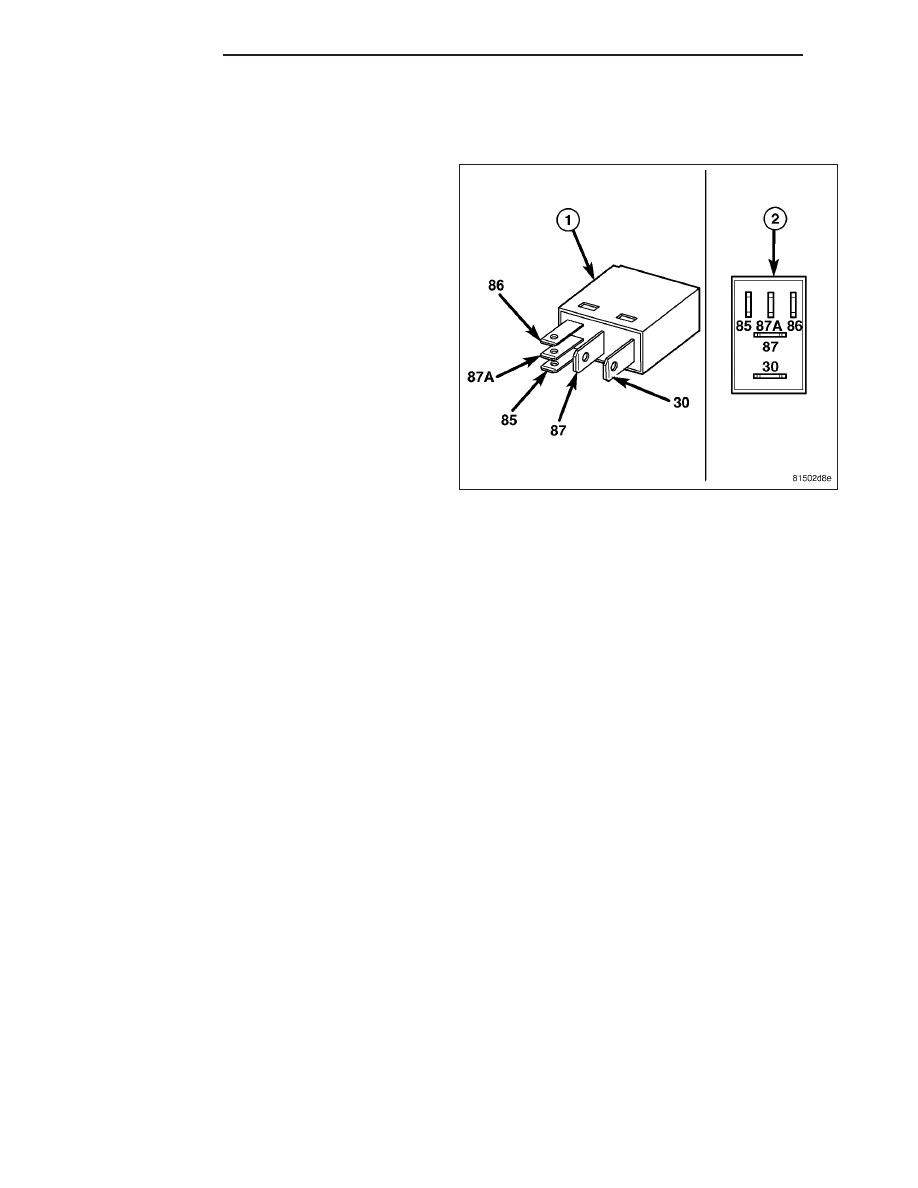
RELAY-A/C CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The A/C clutch relay (1) is an International Standards
Organization (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to
the ISO specifications have common physical dimen-
sions, current capacities, terminal functions and pat-
terns (2). The ISO micro-relay terminal functions are
the same as a conventional ISO relay. However, the
ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is differ-
ent, the current capacity is lower, and the physical
dimensions are smaller than those of the conventional
ISO relay.
The A/C clutch relay is located in the power distribu-
tion center (PDC) in the engine compartment.
OPERATION
The A/C clutch relay is an electromechanical switch that uses a low current input controlled by the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM) or engine contol module (ECM), depending on engine application, to control the high current
output to the A/C clutch field coil. The movable, common feed relay contact is held against the fixed, normally
closed relay contact by spring pressure. When the electromagnetic relay coil is energized, it draws the movable
common feed relay contact away from the fixed, normally closed relay contact and, holds it against the fixed, nor-
mally open relay contact. This action allows high current to flow to the A/C clutch field coil.
When the relay coil is de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable relay contact back against the fixed, nor-
mally closed contact point. The resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the relay coil, and helps to dissipate
voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay coil
collapses.
The A/C clutch relay terminals are connected to the vehicle electrical system through a receptacle in the power
distribution center (PDC). The inputs and outputs of the A/C clutch relay include:
•
The common feed terminal (30) receives battery current through a fuse in the PDC at all times.
•
The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground through the A/C compressor clutch relay control circuit only
when the PCM or ECM electronically pulls the circuit to ground.
•
On gasoline engine applications, the coil battery terminal (86) receives battery current through a fuse in the
junction block only when the ignition switch is in the Run or Start position.
•
On diesel engine applications, the coil battery terminal (86) receives battery current through a fuse in the PDC
at all times.
•
The normally open terminal (87) provides battery current to the A/C clutch coil through the A/C clutch relay
only when the A/C clutch relay coil is energized.
•
The normally closed terminal (87A) is not connected to any circuit in this application, but provides a battery
current output only when the A/C clutch relay coil is de-energized.
The A/C clutch relay cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced. Refer to the appropriate
wiring information for diagnosis and testing of the ISO-standard micro-relay and for complete HVAC wiring diagrams.
24 - 34
CONTROLS
KJ