Jeep Grand Cherokee WJ. Manual - part 57
INSPECTION
The piston is made from a phenolic resin (plastic
material) and should be smooth and clean.
The piston must be replaced if cracked or scored.
Do not attempt to restore a scored piston surface by
sanding or polishing.
CAUTION: If the caliper piston is replaced, install
the same type of piston in the caliper. Never inter-
change phenolic resin and steel caliper pistons.
The pistons, seals, seal grooves, caliper bore and
piston tolerances are different.
The bore can be lightly polished with a brake
hone to remove very minor surface imperfections
(Fig. 83). The caliper should be replaced if the bore is
severely corroded, rusted, scored, or if polishing
would increase bore diameter more than 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch).
ADJUSTMENTS
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH
(1) Press and hold brake pedal in applied position.
(2) Pull switch plunger all the way out to fully
extended position.
(3) Release brake pedal. Then pull pedal lightly
rearward. Pedal will set plunger to correct position
as pedal pushes plunger into switch body. Switch will
make ratcheting sound as it self adjusts.
CAUTION: Booster damage may occur if the pedal
pull exceeds 20 lbs.
PARKING BRAKE SHOE
(1) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(2) Secure rotor with two wheel nuts.
(3) Remove rubber access plug from back of splash
shield.
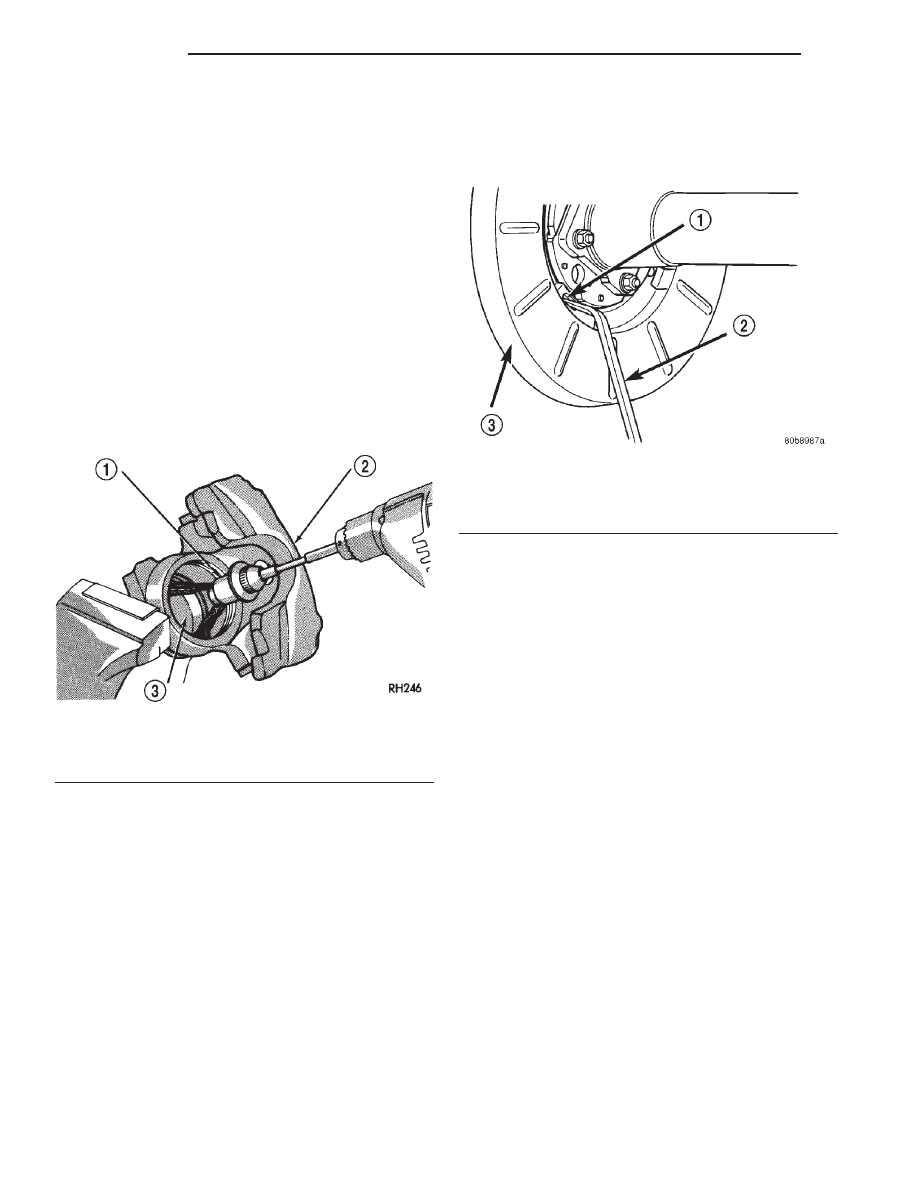
(4) Insert brake tool through access hole in splash
shield (Fig. 84). Position tool at bottom of star wheel.
(5) Rotate star wheel upward direction to expand
shoes (while facing front of vehicle).
(6) Expand shoes until light drag is experienced.
Then back off adjuster screw only enough to elimi-
nate drag.
(7) Install plug in splash shield access hole.
(8) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications and SAE J1703 standards.
No other type of brake fluid is recommended or
approved for usage in the vehicle brake system. Use
only Mopar brake fluid or an equivalent from a
tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-
based fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of
such type fluids will result in seal damage of the
vehicle brake hydraulic system causing a failure of
the vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids
would be items such as engine oil, transmission
fluid, power steering fluid, etc.
Fig. 83 Polishing Piston Bore
1 – SPECIAL HONE
2 – CALIPER
3 – PISTON BORE
Fig. 84 Park Brake Shoe Adjustment
1 – ACCESS HOLE
2 – BRAKE ADJUSTING TOOL
3 – SPLASH SHIELD
5 - 36
BRAKES
WJ
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)