Honda Ridgeline. Manual - part 166
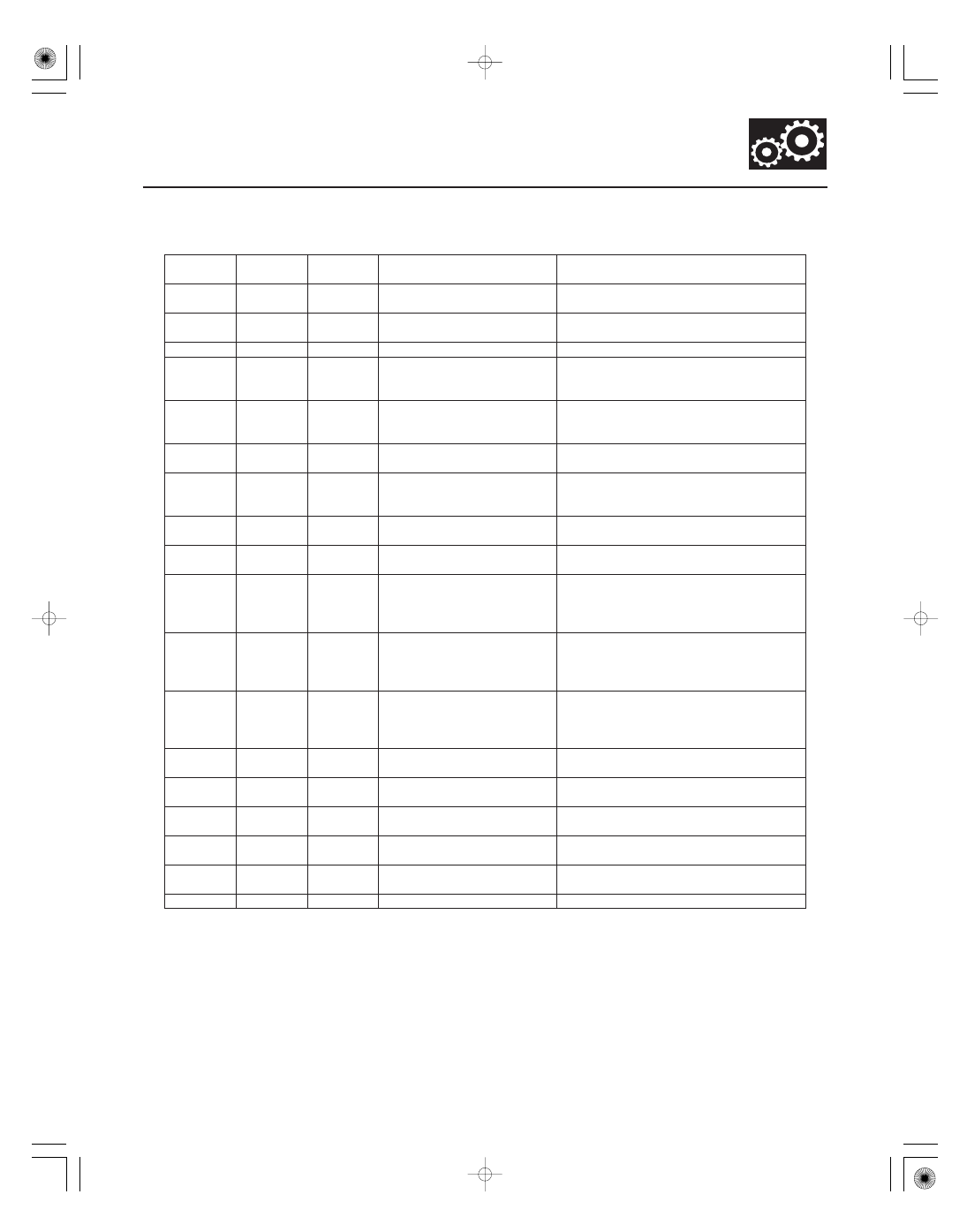
−
−
○
PCM CONNECTOR C
(44P)
Terminal
number
Wire color
Signal
Description
Measuring conditions/Terminal voltage
14-49
•
•
•
•
C9
BLU/RED
EGR
Drives EGR valve
With EGR operating: Duty controlled
With EGR not operation: About 0 V
C13
YEL/BLU
VCC2
Power supply for sensors
With ignition switch to ON (II): About 5.0 V
With ignition switch to LOCK (0): About 0 V
C14
GRN/YEL
SG2
Sensor ground
Less than 1.0 V at all times
C15
BLU/WHT
OP3SW
3rd clutch transmission fluid
pressure switch signal input
With ignition switch to ON (II):
Without 3rd clutch pressure: About 5.0 V
With 3rd clutch pressure: About 0 V
C16
BLU/YEL
OP4SW
4th clutch transmission fluid
pressure switch signal input
With ignition switch to ON (II):
Without 4th clutch pressure: About 5.0 V
With 4th clutch pressure: About 0 V
C17
BLU/YEL
ATP FWD
Transmission range switch D
and 2 positions signal input
In D and 2: About 0 V
In any other positions: Battery voltage
C18
GRN
SH C
Shift solenoid valve C control
With the engine running in 1, and D in 1st,
3rd, and 5th gears: Battery voltage
In P, R, N, 2, and D in 2nd gear: About 0 V
C19
RED
LS A
A/T clutch pressure control
solenoid valve A control
With ignition switch to ON (II): Duty
controlled
C20
WHT/BLK
EGRP
Detects EGR valve position
sensor signal
With engine running: About 1.2
3.0 V
depending on EGR valve lift
C23
GRN/WHT
SH B
Shift solenoid valve B control
With the engine running in P, R, N, 2, and
1, and D in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gears: Battery
voltage
In D in 4th and 5th gears: About 0 V
C25
BLU/YEL
SH A
Shift solenoid valve A control
With the engine running in 2 and 1, and D
in 1st, 2nd, and 5th gears: Battery voltage
In P, R, N, and D in 3rd and 4th gears:
About 0 V
C28
BLU/YEL
ATFT
ATF temperature sensor
signal input
With ignition switch to ON (II): About 0.2
4.0 V (About 1.8 V at normal operating
temperature)
With ignition switch to LOCK (0): About 0 V
C30
WHT
ATP R
Transmission range switch R
position input
In R: About 0 V
In other than R: Battery voltage
C31
RED/BLK
ATP N
Transmission range switch N
position input
In N: About 0 V
In other than N: Battery voltage
C32
YEL/GRN
ATP D
Transmission range switch D
position input
In D: About 0 V
In other than D: Battery voltage
C33
BLU
ATP 2
Transmission range switch 2
position input
In 2: About 0 V
In other than 2: Battery voltage
C34
BRN
ATP 1
Transmission range switch 1
position input
In 1: About 0 V
In other than 1: Battery voltage
C40
BRN/YEL
LG1
Ground
Less than 1.0 V at all times