Honda Odyssey 2004. Manual - part 87
−
*08
*09
*10
15
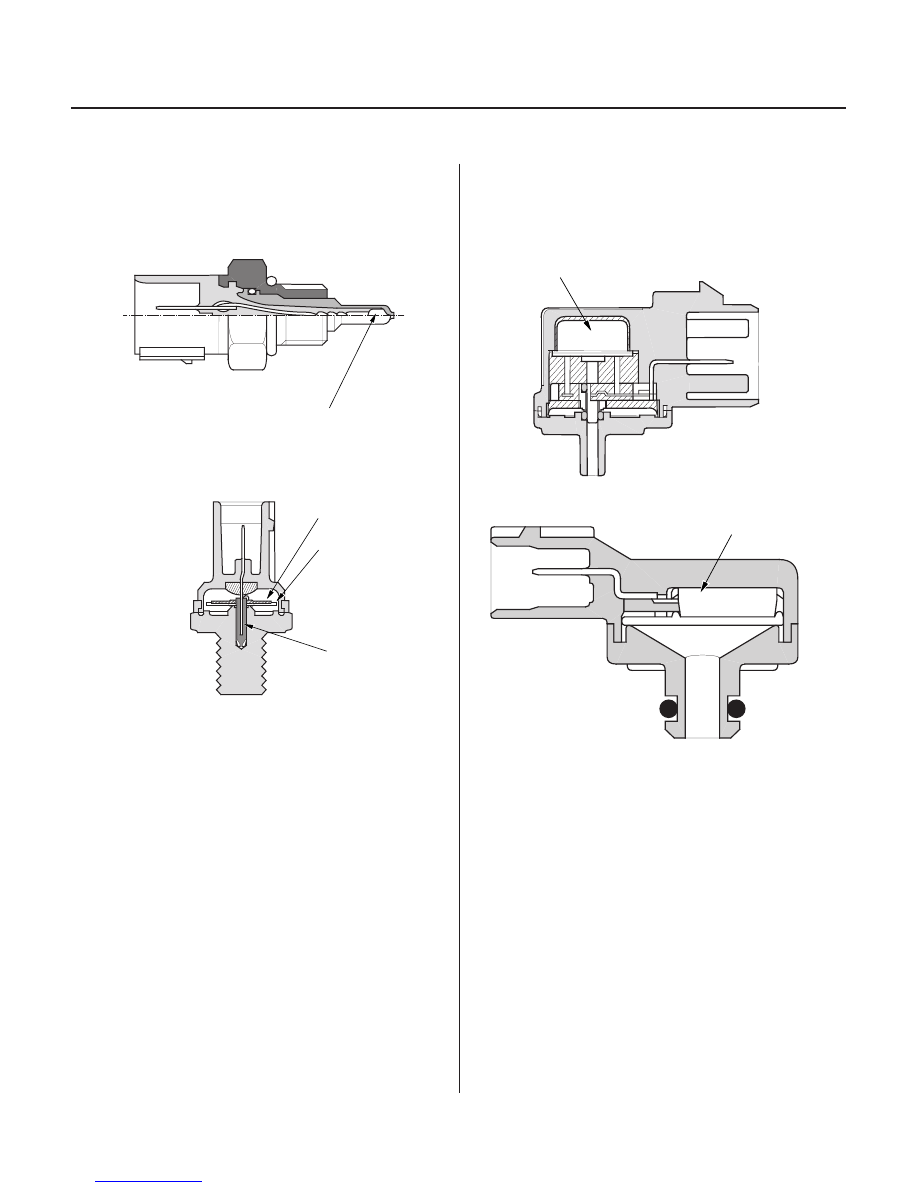
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Knock Sensor
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Indication (In relation
to Readiness Codes) (’01-04 models)
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
’99-00 Models
’01-04 Models
11-46
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Descriptions (cont’d)
THERMISTOR
PIEZO CERAMIC
DIAPHRAGM
TERMINAL
SENSOR UNIT
SENSOR UNIT
The IAT sensor is a temperature dependent resistor
(thermistor). The resistance of the thermistor decreases
as the intake air temperature increases.
The knock control system adjusts the ignition timing for
the octane rating of the gasoline used.
To check if the readiness codes are set to complete,
turn the ignition switch ON (II), but do not start the
engine. The MIL will come on for 15
20 seconds. If it
then goes off, the readiness codes are set to complete.
If it blinks several times, the readiness codes are not set
to complete. To set each code, drive the vehicle or run
the engine as described in the procedures in this
section (see page 11-89).
The MAP sensor converts manifold absolute pressure
into electrical signals to the PCM.
03/07/29 09:18:11 61S0X050_110_0046
The vehicle has certain ‘‘readiness codes’’ that are part
of the on-board diagnostics for the emissions systems.
If the vehicle’s battery has been disconnected or gone
dead, if the DTCs have been cleared, or if the PCM has
been reset, these codes are reset. In some states, part
of the emissions testing is to make sure these codes are
set to complete. If all of them are not set to complete,
the vehicle may fail the test, or the test cannot be
finished.